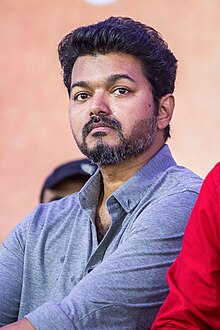Portal:India
Portal maintenance status: (June 2018)
|
Introduction


India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area; the most populous country from June 2023 onwards; and since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. (Full article...)
 Featured article – show another
Featured article – show another
-
Image 1
Freida Selena Pinto (born 18 October 1984) is an Indian actress who has appeared mainly in American and British films. Born and raised in Mumbai, Maharashtra, she resolved at a young age to become an actress. As a student at St. Xavier's College, Mumbai she took part in amateur plays. After graduation, she briefly worked as a model and then as a television presenter.
Pinto rose to prominence with her film debut in the drama Slumdog Millionaire (2008), winning a SAG Award and earning a nomination for the BAFTA Award for Best Supporting Actress. She earned critical acclaim for her roles in Miral (2010), Trishna (2011), and Desert Dancer (2014). She also saw commercial success with the science fiction film Rise of the Planet of the Apes (2011), and the epic fantasy action film Immortals (2011). Pinto's other notable roles include You Will Meet a Tall Dark Stranger (2010), Love Sonia (2018), Hillbilly Elegy (2020), and Mr. Malcolm's List (2022). She also starred in the Showtime miniseries Guerrilla (2017), and had a recurring role in the Hulu series The Path (2018). (Full article...) -
Image 2Portrait by Charles Dana Gibson, c. 1903
Margaret Ives Abbott (June 15, 1878 – June 10, 1955) was an American amateur golfer. She was the first American woman to win an Olympic event: the women's golf tournament at the 1900 Summer Olympics.
Born in Calcutta (now Kolkata), British Raj, in 1878, Abbott moved with her family to Chicago in 1884. She joined the Chicago Golf Club in Wheaton, Illinois, where she received coaching from Charles B. Macdonald and H. J. Whigham. In 1899, she traveled with her mother to Paris to study art. The following year, along with her mother, she signed up for a women's golf tournament without realizing that it was the second modern Olympics. Abbott won the tournament with a score of 47 strokes; her mother tied for seventh place. Abbott received a porcelain bowl as a prize. (Full article...) -
Image 3
The 2003 Sri Lanka cyclone was a moderately powerful tropical cyclone that produced the worst flooding in Sri Lanka in 56 years. The first storm of the 2003 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, it developed over the Bay of Bengal on May 10. Favorable environmental conditions allowed the system to intensify steadily while moving northwestward. The storm reached peak maximum sustained winds of 140 km/h (85 mph) on May 13, making it a very severe cyclonic storm according to the India Meteorological Department (IMD), which is the official Regional Specialized Meteorological Center for the basin. The cyclone drifted north over the central Bay of Bengal, gradually weakening due to heightened wind shear. Turning eastward, the storm deteriorated to a deep depression on May 16 before it curved northeastward and re-intensified into a cyclonic storm. It came ashore in western Myanmar and dissipated over land the following day.
In the wake of prolonged precipitation during the first half of May, the cyclone produced torrential rains across southwest Sri Lanka while stationary in the central Bay of Bengal. The storm drew extensive moisture that coalesced in the mountainous portion of the island. A station at Ratnapura recorded 366.1 mm (14.41 in) of rainfall in 18 hours on May 17, including 99.8 mm (3.93 in) in one hour. In southwestern Sri Lanka, the rainfall caused flooding and landslides that destroyed 24,750 homes and damaged 32,426 others, displacing about 800,000 people. Overall damage totaled about $135 million (2003 USD), and there were 260 deaths. The cyclone also produced some rainfall in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India and along the country's eastern coast. The storm funneled moisture away from the mainland, which possibly contributed to a heat wave that killed 1,900 people, and dropped heavy rainfall in Myanmar. (Full article...) -
Image 4Pather Panchali (Bengali pronunciation: [pɔtʰer pãtʃali] ⓘ, transl. Song of the Little Road) is a 1955 Indian Bengali-language drama film written and directed by Satyajit Ray in his directoral debut and produced by the Government of West Bengal. It is an adaptation of Bibhutibhushan Bandyopadhyay's 1929 Bengali novel of the same name and features Subir Banerjee, Kanu Banerjee, Karuna Banerjee, Uma Dasgupta, and Chunibala Devi in major roles. The first film in The Apu Trilogy, Pather Panchali depicts the childhood travails of the protagonist Apu and his elder sister Durga amid the harsh village life of their poor family.
The film was shot mainly on location, had a limited budget, featured mostly amateur actors, and was made by an inexperienced crew. Lack of funds led to frequent interruptions in production, which took nearly three years, but the West Bengal government pulled Ray out of debt by buying the film for the equivalent of $60,000, which it turned into a profit of $700,000 by 1980. The sitar player Ravi Shankar composed the film's soundtrack and score using classical Indian ragas. Subrata Mitra was in charge of the cinematography while editing was handled by Dulal Dutta. Following its premiere on 3 May 1955 during an exhibition at New York's Museum of Modern Art, Pather Panchali was released in Calcutta the same year to an enthusiastic reception. A special screening was attended by the Chief Minister of West Bengal and the Prime Minister of India. (Full article...) -
Image 5
Preity G. Zinta (pronounced [ˈpriːt̪i ˈzɪɳʈa]; born 31 January 1975) is an Indian actress and entrepreneur primarily known for her work in Hindi films. After graduating with degrees in English honours and criminal psychology, Zinta made her acting debut in Dil Se.. in 1998, followed by a role in Soldier in the same year. These performances earned her the Filmfare Award for Best Female Debut, and she was later recognised for her role as a teenage single mother in Kya Kehna (2000). She established a career as a leading Hindi film actress of the decade with a variety of character types. Her roles, often deemed culturally defiant, along with her unconventional screen persona won her recognition and several accolades.
Following critically appreciated roles in Chori Chori Chupke Chupke (2001), Dil Chahta Hai (2001), Dil Hai Tumhaara (2002), and Armaan (2003), Zinta received the Filmfare Award for Best Actress for her performance in Kal Ho Naa Ho (2003). She starred in two consecutive annual top-grossing films in India, Koi... Mil Gaya (2003) and Veer-Zaara (2004), and was noted for her portrayal of independent, modern Indian women in Salaam Namaste (2005) and Kabhi Alvida Naa Kehna (2006), top-grossing productions in domestic and overseas markets. For her first international role in the Canadian drama Heaven on Earth (2008) she was awarded the Silver Hugo Award for Best Actress and nominated for the Genie Award for Best Actress. She followed this with a hiatus from acting work for several years, with intermittent appearances such as in her self-produced comeback film, Ishkq in Paris (2013), which failed to leave a mark. (Full article...) -
Image 6Kaif promoting Bharat in 2019
Katrina Kaif (pronounced [kəˈʈriːna kɛːf]; born Katrina Turquotte, 16 July 1983) is a British actress who works in Hindi-language films. One of the highest-paid actresses in India, she has received accolades, including four Screen Awards and four Zee Cine Awards, in addition to three Filmfare nominations. Though reception to her acting has varied, she is noted for her action film roles and her dancing ability.
Born in British Hong Kong, Kaif lived in several countries before she moved to London for three years. She received her first modelling assignment as a teenager and later pursued a career as a fashion model. At a fashion show in London, Indian filmmaker Kaizad Gustad cast her in Boom (2003), a critical and commercial failure. While Kaif established a successful modelling career in India, she initially had difficulty finding film roles due to her poor command of Hindi. After appearing in the Telugu film Malliswari (2004), Kaif earned commercial success in Bollywood with the romantic comedies Maine Pyaar Kyun Kiya? (2005) and Namastey London (2007). Further success followed with a series of box-office hits, but she was criticised for her acting, repetitive roles, and inclination to male-dominated films. (Full article...) -
Image 7

Nyctibatrachus major, the Malabar night frog, large wrinkled frog, or Boulenger's narrow-eyed frog is a species of frog in the family Nyctibatrachidae, commonly known as the robust frogs. It was described in 1882 by the zoologist George Albert Boulenger, and is the type species of the genus Nyctibatrachus. It is a large frog for its genus, with an adult snout–vent length of 31.5–52.0 mm (1.24–2.05 in) for males and 43.7–54.2 mm (1.72–2.13 in) for females. It is mainly brownish to greyish in colour, with a dark greyish-brown upperside, a greyish-white underside, and light grey sides. It also has a variety of grey or brown markings. When preserved in ethanol, it is mostly greyish-brown to grey, with whitish sides. Sexes can be told apart by the presence of the femoral glands (bulbous glands near the inner thigh) in males.
The species is endemic to the Western Ghats mountain range of India, where it is found in Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka. Adults inhabit fast-moving forest streams at elevations of up to 900 m (3,000 ft) and have highly specific habitat requirements. Adults are mostly found in or near water and are nocturnal; subadults can be found during both the night and day. Its diet mainly consists of other frogs and insect larvae. Over a period of several days or weeks, females lay multiple small clutches of eggs on leaves and rocks overhanging water; tadpoles drop into the water below on hatching. The species is currently classified as being vulnerable on the IUCN Red List owing to its small and fragmented range and ongoing habitat degradation. Threats to the species include habitat loss, increased human presence near the streams it inhabits, and possibly nitrate pollution caused by fertiliser overuse. (Full article...) -
Image 8Basohli miniature, c. 1730. National Museum, New Delhi
Ganesha (/gəɳeɕᵊ/, Sanskrit: गणेश, IAST: Gaṇeśa), also spelled Ganesh, and also known as Ganapati, Vinayaka, Pillaiyar, and Lambodara, is one of the best-known and most worshipped deities in the Hindu pantheon and is the Supreme God in the Ganapatya sect. His depictions are found throughout India. Hindu denominations worship him regardless of affiliations. Devotion to Ganesha is widely diffused and extends to Jains and Buddhists and beyond India.
Although Ganesha has many attributes, he is readily identified by his elephant head and four arms. He is widely revered, more specifically, as the remover of obstacles and bringer of good luck; the patron of arts and sciences; and the deva of intellect and wisdom. As the god of beginnings, he is honoured at the start of rites and ceremonies. Ganesha is also invoked during writing sessions as a patron of letters and learning. Several texts relate anecdotes associated with his birth and exploits. (Full article...) -
Image 9A female African bush elephant in Mikumi National Park, Tanzania
Elephants are the largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant (Loxodonta africana), the African forest elephant (L. cyclotis), and the Asian elephant (Elephas maximus). They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and the order Proboscidea; extinct relatives include mammoths and mastodons. Distinctive features of elephants include a long proboscis called a trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, pillar-like legs, and tough but sensitive grey skin. The trunk is prehensile, bringing food and water to the mouth and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants have smaller ears and convex or level backs.
Elephants are scattered throughout sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and Southeast Asia and are found in different habitats, including savannahs, forests, deserts, and marshes. They are herbivorous, and they stay near water when it is accessible. They are considered to be keystone species, due to their impact on their environments. Elephants have a fission–fusion society, in which multiple family groups come together to socialise. Females (cows) tend to live in family groups, which can consist of one female with her calves or several related females with offspring. The leader of a female group, usually the oldest cow, is known as the matriarch. (Full article...) -
Image 10
Arthur Edward Jeune Collins (18 August 1885 – 11 November 1914) was an English cricketer and soldier. He held, for 116 years, the record of highest score in cricket: as a 13-year-old schoolboy, he scored 628 not out over four afternoons in June 1899. Collins's record-making innings drew a large crowd and increasing media interest; spectators at the Old Cliftonian match being played nearby were drawn away to watch the junior school house cricket match in which Collins was playing. Despite this achievement, Collins never played first-class cricket. Collins's 628 not out stood as the record score until January 2016 when an Indian boy, Pranav Dhanawade, scored 1009 in a single innings.
Collins joined the British Army in 1902 and studied at the Royal Military Academy, Woolwich, before becoming an officer in the Royal Engineers. He served in France during the First World War, where he was killed in action in 1914 during the First Battle of Ypres. Collins had been mentioned in despatches and also represented the Royal Military Academy at cricket and rugby union. (Full article...) -
Image 11Procession march held on 21 February 1952 in Dhaka
The Bengali language movement was a political movement in East Bengal (modern-day Bangladesh) in 1952, advocating the recognition of the Bengali language as a co-lingua franca of the then-Dominion of Pakistan to allow its use in government affairs, the continuation of its use as a medium of education, its use in media, currency and stamps, and to maintain its writing in the Bengali alphabet / Bengali script
When the Dominion of Pakistan was formed after the separation of the Indian subcontinent in 1947, when the British left, it was composed of various ethnic and linguistic groups, with the geographically non-contiguous East Bengal province having a mainly ethnic Bengali population. In 1948, the Government of the Dominion of Pakistan ordained as part of Islamization of East Pakistan or East Bengal that Urdu will be the sole federal language, alternately Bengali writing in the Perso-Arabic script or Roman script (Romanisation of Bengali) or Arabic as the state language of the whole of Pakistan was also proposed, sparking extensive protests among the Bengali-speaking majority of East Bengal. Facing rising sectarian tensions and mass discontent with the new law, the government outlawed public meetings and rallies. The students of the University of Dhaka and other political activists defied the law and organised a protest on 21 February 1952. The movement reached its climax when police killed student demonstrators on that day. The deaths provoked widespread civil unrest. After years of conflict, the central government relented and granted official status to the Bengali language in 1956. (Full article...) -
Image 12Parinda (transl. Bird) is a 1989 Indian Hindi-language crime thriller film directed, produced and distributed by Vidhu Vinod Chopra. The film stars Jackie Shroff, Anil Kapoor, Nana Patekar and Madhuri Dixit. The story and scenario were written by Chopra, while Shiv Kumar Subramaniam and Imtiyaz Husain wrote the screenplay and dialogues, respectively. R. D. Burman composed the music and Khurshid Hallauri wrote the lyrics. Binod Pradhan served as the film's cinematographer and Renu Saluja was its editor.
Parinda follows Kishan (Shroff), who works for the underworld chieftain Anna (Patekar). Kishan's brother Karan (Kapoor) returns home after completing his studies in the United States. The two brothers are caught on different sides of a gang war after Karan decides to avenge his friend's death by Anna. (Full article...) -
Image 13Margarita with a Straw is a 2014 Indian Hindi-language drama film directed by Shonali Bose. It stars Kalki Koechlin as an Indian teenager with cerebral palsy who relocates to America for her undergraduate education and comes of age following her complex relationship with a blind girl, played by Sayani Gupta. Revathi, Kuljeet Singh, and William Moseley play supporting roles. Produced by Bose in partnership with Viacom18 Motion Pictures, Margarita with a Straw was co-written by Bose and Nilesh Maniyar. The film deals with the challenging concepts of sexuality, inclusion, self-love, and self-acceptance.
Bose conceived the idea for the film in January 2011 during a conversation with Malini Chib, her cousin and a disability rights activist, about the latter's desire to have a normal sex life. Inspired by Chib's story, Bose wrote the first draft of the film's script. After winning a Sundance Mahindra Global Filmmaker Award for the draft, she modified the script to reflect her own perspective, incorporating several personal experiences into the narrative. Bose completed the screenplay with co-writer Maniyar and the advisory council of the Sundance Institute. (Full article...) -
Image 14

Territory of the Western Chalukyas (c. 1100 CE) in India (modern boundaries shown) and the empire's capital, Kalyani, in the modern Bidar district, Karnataka state, India
A large body of Western Chalukya literature in the Kannada language was produced during the reign of the Western Chalukya Empire (973–1200 CE) in what is now southern India. This dynasty, which ruled most of the western Deccan in South India, is sometimes called the Kalyani Chalukya dynasty after its royal capital at Kalyani (now Basavakalyan), and sometimes called the Later Chalukya dynasty for its theoretical relationship to the 6th-century Chalukya dynasty of Badami. For a brief period (1162–1183), the Kalachuris of Kalyani, a dynasty of kings who had earlier migrated to the Karnataka region from central India and served as vassals for several generations, exploited the growing weakness of their overlords and annexed the Kalyani. Around 1183, the last Chalukya scion, Someshvara IV, overthrew the Kalachuris to regain control of the royal city. But his efforts were in vain, as other prominent Chalukya vassals in the Deccan, the Hoysalas, the Kakatiyas and the Seunas destroyed the remnants of the Chalukya power.
Kannada literature from this period is usually categorised into the linguistic phase called Old-Kannada. It constituted the bulk of the Chalukya court's textual production and pertained mostly to writings relating to the socio-religious development of the Jain faith. The earliest well-known writers belonging to the Shaiva faith are also from this period. Under the patronage of Kalachuri King Bijjala II, whose prime minister was the well-known Kannada poet and social reformer Basavanna, a native form of poetic literature called Vachana literature (lit "utterance", "saying" or "sentence") proliferated. The beginnings of the Vachana poetic tradition in the Kannada-speaking region trace back to the early 11th century. Kannada literature written in the champu metre, composed of prose and verse, was popularised by the Chalukyan court poets. However, with the advent of the Veerashaiva (lit, "brave devotees of the god Shiva") religious movement in the mid-12th century, poets favoured the native tripadi (three-line verse composed of eleven ganas or prosodic units), hadugabba (song-poem) and free verse metres for their poems. (Full article...) -
Image 15The political history of medieval Karnataka spans the 4th to the 16th centuries in Karnataka region of India. The medieval era spans several periods of time from the earliest native kingdoms and imperialism; the successful domination of the Gangetic plains in northern India and rivalry with the empires of Tamilakam over the Vengi region; and the domination of the southern Deccan and consolidation against Muslim invasion. The origins of the rise of the Karnataka region as an independent power date back to the fourth-century birth of the Kadamba Dynasty of Banavasi which was the earliest of the native rulers to conduct administration in the native language of Kannada in addition to the official Sanskrit.
In the southern regions of Karnataka, the Western Gangas of Talakad were contemporaries of the Kadambas. The Kadambas and Gangas were followed by the imperial dynasties of the Badami Chalukya Empire, the Rashtrakuta Empire, the Western Chalukya Empire, the Hoysala Empire and the Vijayanagara Empire, all patronising the ancient Indic religions while showing tolerance to the new cultures arriving from the west of the subcontinent. The Muslim invasion of the Deccan resulted in the breaking away of the feudatory Sultanates in the 14th century. The rule of the Bahamani Sultanate of Bidar and the Bijapur Sultanate from the northern Deccan region caused a mingling of the ancient Hindu traditions with the nascent Islamic culture in the region. The hereditary ruling families and clans ably served the large empires and upheld the local culture and traditions. The fall of the Vijayanagara Empire in 1565 brought about a slow disintegration of Kannada-speaking regions into minor kingdoms that struggled to maintain autonomy in an age dominated by foreigners until unification and independence in 1947. (Full article...) -
Image 16
Hrithik Roshan (pronounced [ˈɾɪt̪ɪk ɾoʃən]; born 10 January 1974) is an Indian actor who works in Hindi cinema. He has portrayed a variety of characters and is known for his dancing skills. One of the highest-paid actors in India, he has won many awards, including six Filmfare Awards, of which four were for Best Actor. Starting from 2012, he has appeared in Forbes India's Celebrity 100 several times based on his income and popularity.
Roshan has frequently collaborated with his father, Rakesh Roshan. He made brief appearances as a child actor in several films in the 1980s and later worked as an assistant director on four of his father's films. His first leading role was in the box-office success Kaho Naa... Pyaar Hai (2000), for which he received several awards. Performances in the 2000 terrorism drama Fiza and the 2001 ensemble family drama Kabhi Khushi Kabhie Gham... consolidated his reputation but were followed by several poorly received films. (Full article...) -
Image 17Anbe Sivam (transl. Love Is God) is a 2003 Indian Tamil-language slice-of-life drama film directed by Sundar C and produced by Lakshmi Movie Makers. The film was written by Kamal Haasan, and Madhan provided the dialogues. Anbe Sivam stars Haasan, Madhavan and Kiran Rathod, with Nassar, Santhana Bharathi, Seema and Uma Riyaz Khan playing supporting characters. It tells the story of Nallasivam and Anbarasu, two men of contrasting personalities who undertake an unexpected journey from Bhubaneswar to Chennai.
Produced on a budget of ₹120 million, Anbe Sivam takes on themes such as communism, atheism, and altruism and depicts Haasan's humanist views. The music was composed by Vidyasagar. Arthur A. Wilson served as the cinematographer and M. Prabhaharan served as the art director. (Full article...) -
Image 18Portrait by Alexander Bassano, 1882
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days—which was longer than those of any of her predecessors—constituted the Victorian era. It was a period of industrial, political, scientific, and military change within the United Kingdom, and was marked by a great expansion of the British Empire. In 1876, the British parliament voted to grant her the additional title of Empress of India.
Victoria was the daughter of Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn (the fourth son of King George III), and Princess Victoria of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld. After the deaths of her father and grandfather in 1820, she was raised under close supervision by her mother and her comptroller, John Conroy. She inherited the throne aged 18 after her father's three elder brothers died without surviving legitimate issue. Victoria, a constitutional monarch, attempted privately to influence government policy and ministerial appointments; publicly, she became a national icon who was identified with strict standards of personal morality. (Full article...) -
Image 19
Shah Rukh Khan (pronounced [ˈʃaːɦɾʊx xäːn] ⓘ; born 2 November 1965), also known by the initialism SRK, is an Indian actor and film producer who works in Hindi cinema. Referred to in the media as the "Baadshah of Bollywood" and "King Khan", he has appeared in more than 100 films, and earned numerous accolades, including 14 Filmfare Awards. He has been awarded the Padma Shri by the Government of India, as well as the Order of Arts and Letters and Legion of Honour by the Government of France. Khan has a significant following in Asia and the Indian diaspora worldwide. In terms of audience size and income, several media outlets have described him as one of the most successful film stars in the world. Many of his films thematise Indian national identity and connections with diaspora communities, or gender, racial, social and religious differences and grievances.
Khan began his career with appearances in several television series in the late 1980s and made his Bollywood debut in 1992 with the musical romance Deewana. He was initially recognised for playing villainous roles in the films Baazigar (1993) and Darr (1993). Khan established himself by starring in a series of top-grossing romantic films, including Dilwale Dulhania Le Jayenge (1995), Dil To Pagal Hai (1997), Kuch Kuch Hota Hai (1998), Mohabbatein (2000), Kabhi Khushi Kabhie Gham... (2001), Kal Ho Naa Ho (2003), Veer-Zaara (2004) and Kabhi Alvida Naa Kehna (2006). He earned critical acclaim for his portrayal of an alcoholic in the period romantic drama Devdas (2002), a NASA scientist in the social drama Swades (2004), a hockey coach in the sports drama Chak De! India (2007), and a man with Asperger syndrome in the drama My Name Is Khan (2010). Further commercial successes came with the romances Om Shanti Om (2007) and Rab Ne Bana Di Jodi (2008), and with his expansion to comedies in Chennai Express (2013) and Happy New Year (2014). Following a brief setback and hiatus, Khan made a career comeback with the 2023 action thrillers Pathaan and Jawan, both of which rank among the highest-grossing Indian films. (Full article...) -
Image 20
The black stork (Ciconia nigra) is a large bird in the stork family Ciconiidae. It was first described by Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of his Systema Naturae. Measuring on average 95 to 100 cm (37 to 39 in) from beak tip to end of tail with a 145-to-155 cm (57-to-61 in) wingspan, the adult black stork has mainly black plumage, with white underparts, long red legs and a long pointed red beak. A widespread but uncommon species, it breeds in scattered locations across Europe (predominantly in Portugal and Spain, and central and eastern parts), and east across the Palearctic to the Pacific Ocean. It is a long-distance migrant, with European populations wintering in tropical Sub-Saharan Africa, and Asian populations in the Indian subcontinent. When migrating between Europe and Africa, it avoids crossing broad expanses of the Mediterranean Sea and detours via the Levant in the east, the Strait of Sicily in the center, or the Strait of Gibraltar in the west. An isolated non-migratory population lives in Southern Africa.
Unlike the closely related white stork, the black stork is a shy and wary species. It is seen singly or in pairs, usually in marshy areas, rivers or inland waters. It feeds on amphibians, small fish and insects, generally wading slowly in shallow water stalking its prey. Breeding pairs usually build nests in large forest trees—most commonly deciduous but also coniferous—which can be seen from long distances, as well as on large boulders, or under overhanging ledges in mountainous areas. The female lays two to five greyish-white eggs, which become soiled over time in the nest. Incubation takes 32 to 38 days, with both sexes sharing duties, and fledging takes 60 to 71 days. (Full article...) -
Image 21
Muhammad Ali Jinnah (born Mahomedali Jinnahbhai; 25 December 1876 – 11 September 1948) was a barrister, politician, and the founder of Pakistan. Jinnah served as the leader of the All-India Muslim League from 1913 until the inception of Pakistan on 14 August 1947 and then as Pakistan's first governor-general until his death.
Born at Wazir Mansion in Karachi, Jinnah was trained as a barrister at Lincoln's Inn in London, England. Upon his return to India, he enrolled at the Bombay High Court, and took an interest in national politics, which eventually replaced his legal practice. Jinnah rose to prominence in the Indian National Congress in the first two decades of the 20th century. In these early years of his political career, Jinnah advocated Hindu–Muslim unity, helping to shape the 1916 Lucknow Pact between the Congress and the All-India Muslim League, in which Jinnah had also become prominent. Jinnah became a key leader in the All-India Home Rule League, and proposed a fourteen-point constitutional reform plan to safeguard the political rights of Muslims in the Indian subcontinent. In 1920, however, Jinnah resigned from the Congress when it agreed to follow a campaign of satyagraha, which he regarded as political anarchy. (Full article...) -
Image 22Ganges river dolphin breaking the surface
South Asian river dolphins are toothed whales in the genus Platanista, which inhabit the waterways of the Indian subcontinent. They were historically considered to be one species (P. gangetica) with the Ganges river dolphin and the Indus river dolphin being subspecies (P. g. gangetica and P. g. minor respectively). Genetic and morphological evidence led to their being described as separate species in 2021. The Ganges and Indus river dolphins are estimated to have diverged 550,000 years ago. They are the only living members of the family Platanistidae and the superfamily Platanistoidea. Fossils of ancient relatives date to the late Oligocene.
South Asian river dolphins are small but stocky cetaceans with long snouts or rostra, broad flippers, and small dorsal fins. They have several unusual features. Living in murky river waters, they have eyes that are tiny and lensless; the dolphins rely instead on echolocation for navigation. The skull has large crests over the melon, which help direct their echolocation signals. These dolphins prey mainly on fish and shrimp and hunt them throughout the water column. They are active through the day and are sighted in small groups. Both species are listed as endangered by the IUCN Red List of mammals. Major threats include dams, barrages, fishing nets, and both chemical and acoustic pollution. (Full article...) -
Image 23Ahalya by Raja Ravi Varma (1848–1906)
In Hinduism, Ahalya (Sanskrit: अहल्या, IAST: Ahalyā) also spelt as Ahilya, is the wife of the sage Gautama Maharishi. Many Hindu scriptures describe her legend of seduction by the king of the gods Indra, her husband's curse for her infidelity, and her liberation from the curse by the god Rama.
Created by the god Brahma as the most beautiful woman, Ahalya was married to the much older Gautama. In the earliest full narrative, when Indra comes disguised as her husband, Ahalya sees through his disguise but nevertheless accepts his advances. Later sources often absolve her of all guilt, describing how she falls prey to Indra's trickery. In all narratives, Ahalya and Indra are cursed by Gautama. The curse varies from text to text, but almost all versions describe Rama as the eventual agent of her liberation and redemption. Although early texts describe how Ahalya must atone by undergoing severe penance while remaining invisible to the world and how she is purified by offering Rama hospitality, in the popular retelling developed over time, Ahalya is cursed to become a stone and regains her human form after she is brushed by Rama's foot. (Full article...) -
Image 24Mayabazar (transl. Market of illusions) is a 1957 Indian epic Hindu mythological film directed by K. V. Reddy. It was produced by Nagi Reddi and Chakrapani under their banner, Vijaya Productions. The film was shot simultaneously in Telugu and Tamil, with a few differences in the cast. The story is an adaptation of the folk tale Sasirekha Parinayam, which is based on the characters of the epic Mahabharata. It revolves around the roles of Krishna (N. T. Rama Rao) and Ghatotkacha (S. V. Ranga Rao), as they try to reunite Arjuna's son Abhimanyu (Telugu: Akkineni Nageswara Rao, Tamil: Gemini Ganesan) with his love, Balarama's daughter Sasirekha (Savitri). The Telugu version features Gummadi, Mukkamala, Ramana Reddy, and Relangi in supporting roles, with D. Balasubramaniam, R. Balasubramaniam, V. M. Ezhumalai, and K. A. Thangavelu playing those parts in the Tamil version.
The first mythological film produced by their studio, Mayabazar marked a milestone for Nagi Reddi and Chakrapani. In addition to the technical crew, 400 studio workers – including light men, carpenters, and painters – participated in the development of the film. Director Reddy was meticulous with the pre-production and casting phases, which took nearly a year to complete. Though Rama Rao was initially reluctant to play the lead role, his portrayal of Krishna received acclaim and yielded more offers to reprise the same role in several unrelated films. The soundtrack features twelve songs, with most of the musical score composed by Ghantasala. Telugu lyrics were written by Pingali Nagendrarao and Tamil lyrics were written by Thanjai N. Ramaiah Dass. One of those songs, Lahiri Lahiri, was accompanied by the first illusion of moonlight in Indian cinema, shot by cinematographer Marcus Bartley. (Full article...) -
Image 25

India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area; the most populous country from June 2023 onwards; and since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia.
Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago. Their long occupation, predominantly in isolation as hunter-gatherers, has made the region highly diverse, second only to Africa in human genetic diversity. Settled life emerged on the subcontinent in the western margins of the Indus river basin 9,000 years ago, evolving gradually into the Indus Valley Civilisation of the third millennium BCE. By 1200 BCE, an archaic form of Sanskrit, an Indo-European language, had diffused into India from the northwest. Its hymns recorded the dawning of Hinduism in India. India's pre-existing Dravidian languages were supplanted in the northern regions. By 400 BCE, caste had emerged within Hinduism, and Buddhism and Jainism had arisen, proclaiming social orders unlinked to heredity. Early political consolidations gave rise to the loose-knit Maurya and Gupta Empires. Widespread creativity suffused this era, but the status of women declined, and untouchability became an organized belief. In South India, the Middle kingdoms exported Dravidian language scripts and religious cultures to the kingdoms of Southeast Asia. (Full article...)
Selected pictures
-
Image 1
 Coin design credit: East India Company and the Calcutta Mint; photographed by Andrew ShivaThe mohur is a gold coin that was formerly minted by several governments, including those of British India. It was usually equivalent in value to fifteen silver rupees. Gold mohurs issued by the British East India Company or the Crown are valuable collectors' items, and sell in auctions for high prices. The double mohur (minted between 1835 and 1918), with a value of thirty rupees, is the highest-denomination circulating coin ever issued in India. The 1835 two-mohur coin above was minted in the reign of King William IV, while the 1862 one-mohur coin below was minted in the reign of Queen Victoria; both are now part of the National Numismatic Collection at the National Museum of American History.
Coin design credit: East India Company and the Calcutta Mint; photographed by Andrew ShivaThe mohur is a gold coin that was formerly minted by several governments, including those of British India. It was usually equivalent in value to fifteen silver rupees. Gold mohurs issued by the British East India Company or the Crown are valuable collectors' items, and sell in auctions for high prices. The double mohur (minted between 1835 and 1918), with a value of thirty rupees, is the highest-denomination circulating coin ever issued in India. The 1835 two-mohur coin above was minted in the reign of King William IV, while the 1862 one-mohur coin below was minted in the reign of Queen Victoria; both are now part of the National Numismatic Collection at the National Museum of American History. -
Image 2Photograph credit: Bourne & Shepherd; retouched by Yann ForgetThe Rudra Mahalaya Temple is an ancient temple complex at Siddhpur in the Patan district of Gujarat, India. The temple was completed in 1140 by Jayasimha Siddharaja, but in 1296, Alauddin Khalji sent an army under Ulugh Khan and Nusrat Khan, who dismantled the structure. In 1414 or 1415, the temple was further destroyed and the western part was converted into a congregational mosque by Muslim ruler Ahmad Shah I of the Muzaffarid dynasty. Apart from the mosque, the surviving fragments consist of two porches, a torana (ornamental gateway) and a few pillars.
-
Image 3Photo credit: PeripitusThe national flower of India, Nelumbo nucifera is known by a number of common names, including Indian lotus, sacred lotus, bean of India, and sacred water-lily. This plant is an aquatic perennial, though under favorable conditions its seeds may remain viable for many years.
-
Image 4Photograph: Muhammad Mahdi KarimAlstroemeria × hybrida, an Alstroemeria hybrid, at the Lal Bagh Botanical Gardens in Bangalore, India. The genus consists of some 120 species and is native to South America.
-
Image 5The mosque at the Taj Mahal complex in Agra, India. This red sandstone building, on the western side of the complex, faces the west side of the mausoleum. In the forefront is a howz, meant for ablution. On the eastern side of the complex is the jawab ("answer"), a mirror image of the mosque except for the missing mihrab and different floor pattern; this jawab was mainly intended for architectural balance. Both were constructed in 1643.
-
Image 6Photograph: Yann; edit: Jim CarterA view of the Taj Mahal from the south, featuring the Charbagh garden. The mausoleum complex also includes subsidiary tombs, waterworks infrastructure, the small town of Taj Ganji, and a "moonlight garden". Its origins and architecture have been extensively documented, covering both the circumstances of its commission and the cultural and historical influence of the Islamic Mughal Empire in India.
-
Image 7Photo: YannWomen of the Gondi, the largest tribe of Indian aboriginals in central India. They are classified as a Scheduled Tribe in most Indian states. The Gondi language is related to Telugu and other Dravidian languages. About half of Gonds speak Gondi languages, while the rest speak Indo-Aryan languages including Hindi. For many years during the British colonial period, the Gonds were considered to have performed human sacrifices, although this notion was later discredited.
-
Image 8Photograph: Augustus BinuOdissi is an ancient classical dance that originated in the Hindu temples of Odisha, India. Historically, it has been performed predominantly by women, and expressed religious stories and spiritual ideas, particularly of Vaishnavism (Vishnu as Jagannath), but also of other traditions such as those related to Hindu gods Shiva and Surya, as well as Hindu goddesses (Shaktism). Modern Odissi productions by Indian artists have presented a diverse range of experimental ideas, culture fusion, themes and plays.
Odissi is learnt and performed as a composite of a basic dance motif called the Bhangas (symmetric body bends, stance). It involves the lower, mid, and upper body as three sources of perfecting expression and audience engagement with geometric symmetry and rhythmic musical resonance. -
Image 9Papilio demoleus matingPhotograph: JkadavoorA mating pair of Papilio demoleus, a common and widespread Swallowtail butterfly, photographed at Kadavoor, Kerala, India. After successful mating the female goes from plant to plant, laying a single egg at a time on top of a leaf, and flies off as soon as the egg is laid.
-
Image 10Photograph: Muhammad Mahdi KarimA panoramic view of Bangalore from Corporation Circle, with UB City to the left and Richmond area to the right. Kanteerava Indoor Stadium is in the foreground. The third largest city in India, the city is known as the Silicon Valley of India for its numerous IT exports.
-
Image 11Photograph credit: Charles James SharpDanaus genutia, the common tiger or striped tiger, is a species of brush-footed butterfly found in Sri Lanka, India, Myanmar, south-eastern Asia and Australia. It prefers areas of moderate to heavy rainfall, and typical habitats include scrubby jungle, deciduous forests and fallow land near habitations. The insect sequesters toxins from plants, and advertises its unpalatability by having prominent markings and striking colour patterns. This adult male common tiger, of the subspecies D. g. genutia, was photographed in Kerala, India.
-
Image 12Photograph credit: Rucha Karkarey; edited by John HarrisonThe round ribbontail ray (Taeniura meyeni) is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae, found throughout the nearshore waters of the tropical Indo-Pacific region. Reaching 1.8 m (6 ft) across, this large ray is characterized by a thick, rounded pectoral fin disc covered by small tubercles on top, and a relatively short tail bearing a single venomous spine. The ray is well-camouflaged when lying on the seabed; it is largely nocturnal, and preys on molluscs, crustaceans and bony fish. Mature females bear litters of up to seven pups, which are fed during gestation on "uterine milk", a product secreted by the walls of the oviduct. This round ribbontail ray was photographed in Lakshadweep, India.
-
Image 13Photograph credit: Jeevan JoseLeptosia nina, known as the psyche, is a species of butterfly in the family Pieridae (the sulphurs, yellows and whites), found in the Indian subcontinent, southeastern Asia, and Australia. It has a small wingspan of 2.5 to 5 cm (1 to 2 in). The upper side of the otherwise white forewing has a large, somewhat pear-shaped, black spot; this spot is also present on the underside which is scattered with greenish dots and speckles, sometimes arranged in bands. This L. nina butterfly was photographed in Kerala, India.
-
Image 14Photograph: Augustus BinuChandiroor Divakaran (b. 1946) is a Malayalam–language poet and folk song writer from Kerala, India. He has published numerous collections of poetry since his debut collection, Radha, in 1965.
-
Image 15Photo: Muhammad Mahdi KarimThe glass house at Lal Bagh, a botanical garden in Bangalore, India. The garden was commissioned by the ruler of Mysore, Hyder Ali in 1760, and completed during the reign of his son Tipu Sultan. The glass house was modeled on London's Crystal Palace and constructed at the end of the 19th century.
 Featured list – show another
Featured list – show another
-
Image 1
The Jnanpith Award is the oldest and the highest Indian literary award presented annually by the Bharatiya Jnanpith to an author for their "outstanding contribution towards literature". Instituted in 1961, the award is bestowed only on Indian writers writing in Indian languages included in the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India and English, with no posthumous conferral.
From 1965 till 1981, the award was given to the authors for their "most outstanding work" and consisted of a citation plaque, a cash prize and a bronze replica of Saraswati, the Hindu goddess of knowledge and wisdom. The first recipient of the award was the Malayalam writer G. Sankara Kurup who received the award in 1965 for his collection of poems, Odakkuzhal (The Bamboo Flute), published in 1950. The rules were revised in subsequent years to consider only works published during the preceding twenty years, excluding the year for which the award was to be given and the cash prize was increased to ₹1.5 lakh (equivalent to ₹31 lakh or US$35,000 in 2023) from 1981. (Full article...) -
Image 2
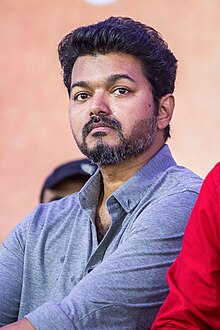
Vijay in 2018 in Nadigar Sangam Protest
Vijay is an Indian actor, playback singer and politician who works in Tamil cinema. He made his cinematic debut in 1984 with Vetri, directed by his father, S. A. Chandrasekhar. After appearing in Chandrasekhar's films as a child artist, Vijay made his debut as a lead actor with Naalaiya Theerpu (1992) at the age of 18. He followed it with a role opposite Vijayakanth in Senthoorapandi (1993). Vijay went on to play lead roles in his father's directorial ventures such as Rasigan (1994) and Deva (1995)Vishnu Most of those films were successful commercially.
Vijay's first commercial blockbuster was romcom Coimbatore Mappillai in 1996, followed by his breakthrough blockbuster romance film, Poove Unakkaga. His subsequent films, Love Today (1997) and Kadhalukku Mariyadhai (1997), were critically and commercially successful. His performance in the latter won him the Tamil Nadu State Film Award for Best Actor. Thulladha Manamum Thullum (1999), where he played a passionate singer gained him the reputation of a romantic hero. (Full article...) -
Image 3

Members of the Indian cricket team before a Women's World Twenty20 game in Sydney, 2009.
A women's Twenty20 International (WT20I) is a 20 overs-per-side cricket match played in a maximum of 150 minutes between two ICC member sides, and is played under the rules of Twenty20 cricket. The first such match was held in August 2004 between England and New Zealand. The India women's national cricket team played its first WT20I against England in August 2006; India won the match by eight wickets.
Since the team made its first WT20I appearance in 2006, 73 players—including five different captains—have represented India in the format. The list is arranged in the order in which each player won her first Twenty20 cap. Where more than one player won her first Twenty20 cap in the same match, those players are listed alphabetically by surname. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Sanjay Dutt at Mumbai Airport
Sanjay Dutt is an Indian actor known for his work in Hindi films as well as a few Telugu, Kannada, Tamil, and Punjabi films. He made his acting debut in 1981, opposite Tina Ambani, in his father Sunil Dutt's romantic action film Rocky (1981). Rocky was ranked at tenth highest-grossing Bollywood films of 1981. After appearing in a series of box office flops, he starred in Mahesh Bhatt's crime thriller film Naam (1986). Dutt received critical acclaim for his performance, and it became a turning point in his career.
In 1991, Dutt appeared in Lawrence D'Souza's Indian romantic drama film Saajan (1991), starring alongside Madhuri Dixit and Salman Khan. For his performance, Dutt was nominated for the Filmfare Award for Best Actor. He was nominated again for the same award for his performance in Khalnayak (1993). Dutt won the Filmfare Award for Best Actor—for portraying a young man who later becomes a gangster in Vaastav: The Reality (1999). He also received critical acclaim for his performance. Dutt next appeared in Vidhu Vinod Chopra's crime thriller film Mission Kashmir (2000). For his performance, Dutt was nominated for the Filmfare Award for Best Actor. (Full article...) -
Image 5Zindagi Na Milegi Dobara (English: You Live Only Once) is a 2011 Indian coming-of-age film directed by Zoya Akhtar, who also co-wrote the film along with Reema Kagti. It is produced by Excel Entertainment. The film stars an ensemble cast of Hrithik Roshan, Abhay Deol and Farhan Akhtar, with Katrina Kaif and Kalki Koechlin in supporting roles. The musical score for the film was composed by the trio Shankar–Ehsaan–Loy. Its cinematography was provided by Carlos Catalan. The film narrates the story of three friends on a bachelor trip and how each of them discover themselves and overcome their problems and insecurities.
Made on a budget of ₹550 million (US$6.4 million), Zindagi Na Milegi Dobara was released on 5 July 2011 and grossed over ₹1.53 billion (US$18 million) worldwide. Rotten Tomatoes, a review aggregator, surveyed 7 reviews and judged 100 percent to be positive. The film garnered awards and nominations in several categories, with particular praise for its direction, screenplay, and the performances of its cast. As of 2015, the film has won 33 awards from 66 nominations. (Full article...) -
Image 6

Basu at the audio release of Creature 3D
Bipasha Basu is an Indian actress who has featured in over 50 films, predominantly in Hindi language. After a successful career as a model, she made her film debut with a supporting role in Abbas–Mustan's thriller Ajnabee (2001), which won her the Filmfare Award for Best Female Debut. Basu followed this with a role in her first Telugu cinema—the action film Takkari Donga (2002). She had her first major success with the supernatural thriller Raaz (2002), which earned Basu her first Filmfare Award for Best Actress nomination. The following year, she starred opposite John Abraham in the erotic thriller Jism, in which she played a seductive wife. She received a Filmfare Award for Best Performance in a Negative Role nomination for the film. Her roles in these films established her as a sex symbol.
Basu followed this initial success with roles in a series of commercial failures, including the thrillers Aetbaar, Rudraksh, Rakht—all in 2004—and the romance Barsaat (2005). She later featured in Prakash Jha's crime drama Apaharan (2005) and the ensemble comedy No Entry (2005). The latter emerged as a financial success, grossing ₹750 million (US$8.7 million) at the box office, and Basu's role of an escort earned her a nomination for the Best Supporting Actress at the 51st Filmfare Awards. Basu had seven film releases in 2006. Her role as an executive at a conglomerate in Madhur Bhandarkar's drama Corporate earned her another nomination for the Filmfare Award for Best Actress. She then portrayed a character based on Bianca in Vishal Bhardwaj's Omkara, an adaptation of the Shakespearean tragedy Othello. In Sanjay Gadhvi's action film Dhoom 2—her final release of the year—she played dual roles; it was the top-grossing Bollywood film of the year. In 2008, she collaborated with Abbas–Mustan for the second time for Race. Her performance as a troubled wife in Rituparno Ghosh's 2009 Bengali film Shob Charitro Kalponik was critically acclaimed. She then featured in the third installment of the Raaz series, entitled Raaz 3D (2012). Due to her frequent associations with horror films, she was labelled India's "horror queen" by the media. (Full article...) -
Image 7

The Wanderers Stadium, Johannesburg, where India played their first ever Twenty20 International
A Twenty20 International (T20I) is a form of cricket match between two representative teams, each having T20I status as determined by the International Cricket Council (ICC), and is played under the rules of Twenty20 cricket. The first such match was played between Australia and New Zealand on 17 February 2005. The Indian cricket team played its first T20I match—under the captaincy of Virender Sehwag—during the 2006–07 series in South Africa; India defeated the hosts by six wickets in the one-off match and claimed the series.
As of July 2024, 115 players have represented India in T20Is. India won the inaugural edition of the ICC World Twenty20, defeating Pakistan in the final by five runs. (Full article...) -
Image 8

Rabindranath Tagore was the first person of Indian origin and also first Asian to be awarded with the Nobel Prize. He received the prize for Literature in 1913.
The Nobel Prize is a set of annual international awards bestowed on "those who conferred the greatest benefit on humankind" in the fields of Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, Peace and Economic Sciences, instituted by Alfred Nobel's last will, which specified that a part of his fortune be used to create the prizes. Each laureate (recipient) receives a gold medal, a diploma and a sum of money, which is decided annually by the Nobel Foundation. The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences awards the Nobel Prize in Physics, the Nobel Prize in Chemistry and the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel; the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute awards the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine; the Swedish Academy awards the Nobel Prize in Literature; and the Norwegian Nobel Committee awards the Nobel Peace Prize. They are widely recognised as one of the most prestigious honours awarded in the aforementioned fields.
First instituted in 1901, the Nobel Prize has been awarded to a total of 989 individuals (930 men and 59 women) and 30 organisations as of 2022[update]. Among the recipients, 12 are Indians of which 5 are Indian citizens and 7 are of Indian ancestry or residency. Rabindranath Tagore was the first Indian citizen to be awarded and also first Asian to be awarded in 1913. Mother Teresa is the only woman among the list of recipients. Sri Aurobindo, the Indian poet, philosopher, nationalist and developer of Integral yoga, was nominated unsuccessfully for the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1943 and for the Nobel Peace Prize in 1950. (Full article...) -
Image 9

The Padma Bhushan is the third-highest civilian award of the Republic of India. Instituted on 2 January 1954, the award is given for "distinguished service of a high order", without distinction of race, occupation, position, or sex. The recipients receive a Sanad, a certificate signed by the President of India and a circular-shaped medallion with no monetary association. The recipients are announced every year on Republic Day (26 January) and registered in The Gazette of India—a publication used for official government notices and released weekly by the Department of Publication, under the Ministry of Urban Development. The conferral of the award is not considered official without its publication in the Gazette. The names of recipients whose awards have been revoked or restored, both of which processes require the authority of the president, are archived and they are required to surrender their medal when their name is struck from the register; none of the conferments of Padma Bhushan during 2000–2009 have been revoked or restored. The recommendations are received from all the state and the union territory governments, as well as from Ministries of the Government of India, the Bharat Ratna and the Padma Vibhushan awardees, the Institutes of Excellence, the Ministers, the Chief Ministers and the Governors of State, and the Members of Parliament including private individuals.
When instituted in 1954, the Padma Bhushan was classified as "Dusra Varg" (Class II) under the three-tier Padma Vibhushan awards, which were preceded by the Bharat Ratna in hierarchy. On 15 January 1955, the Padma Vibhushan was reclassified into three different awards as the Padma Vibhushan, the Padma Bhushan and the Padma Shri. The criteria included "distinguished service of a high order in any field including service rendered by Government servants", but excluded those working with the public sector undertakings with the exception of doctors and scientists. The 1954 statutes did not allow posthumous awards; this was subsequently modified in the January 1955 statute. The design was also changed to the form that is currently in use; it portrays a circular-shaped toned bronze medallion 1+3⁄4 inches (44 mm) in diameter and 1⁄8 inch (3.2 mm) thick. The centrally placed pattern made of outer lines of a square of 1+3⁄16 inches (30 mm) side is embossed with a knob carved within each of the outer angles of the pattern. A raised circular space of diameter 1+1⁄16 inches (27 mm) is placed at the centre of the decoration. A centrally located lotus flower is embossed on the obverse side of the medal and the text "Padma" is placed above and the text "Bhushan" is placed below the lotus written in Devanagari script. The State Emblem of India is displayed in the centre of the reverse side, together with the national motto of India, "Satyameva Jayate" (Truth alone triumphs) in Devanagari script, which is inscribed on the lower edge. The rim, the edges and all embossing on either side is of standard gold with the text "Padma Bhushan" of gold gilt. The medal is suspended by a pink riband 1+1⁄4 inches (32 mm) in width with a broad white stripe in the middle. It is ranked fifth in the order of precedence of wearing of medals and decorations of the Indian civilian and military awards. (Full article...) -
Image 10

The Padma Bhushan is the third-highest civilian award of the Republic of India. Instituted on 2 January 1954, the award is given for "distinguished service of a high order", without distinction of race, occupation, position, or sex. The recipients receive a Sanad, a certificate signed by the President of India and a circular-shaped medallion with no monetary association. The recipients are announced every year on Republic Day (26 January) and registered in The Gazette of India—a publication used for official government notices and released weekly by the Department of Publication, under the Ministry of Urban Development. The conferral of the award is not considered official without its publication in the Gazette. The name of recipient, whose award have been revoked or restored, both of which require the authority of the President, is archived and they are required to surrender their medal when their name is struck from the register; none of the conferments of Padma Bhushan during 1954–1959 have been revoked or restored. The recommendations are received from all the state and the union territory governments, as well as from Ministries of the Government of India, the Bharat Ratna and the Padma Vibhushan awardees, the Institutes of Excellence, the Ministers, the Chief Ministers and the Governors of State, and the Members of Parliament including private individuals.
When instituted in 1954, the Padma Bhushan was classified as "Dusra Varg" (Class II) under the three-tier Padma Vibhushan awards, which were preceded by the Bharat Ratna in hierarchy. The original specification of the award was a circle made of standard silver 1+3⁄8 inches (35 mm) in diameter, with rims on both the sides. A centrally located lotus flower was embossed on the obverse side of the medal and the text "Padma Vibhushan" written in Devanagari script was inscribed above the lotus along the upper edge of the medal. A floral wreath was embossed along the lower edge and a lotus wreath at the top along the upper edge. The State Emblem of India was placed in the centre of the reverse side with the text "Desh Seva" in Devanagari Script on the lower edge. The medal was suspended by a pink riband 1+1⁄4 inches (32 mm) in width divided into three equal segments by two white vertical lines. (Full article...) -
Image 11

Sourav Ganguly had captained Pune Warriors India in the highest number of matches: 15.
Pune Warriors India (PWI) was a Pune-based franchise cricket team that participated in the Indian Premier League (IPL). They played their first Twenty20 match in the 2011 season of the IPL against Kings XI Punjab. PWI played in three editions of the IPL, failing to reach the playoffs on all occasions. They came last in the 2012 IPL, and came second-last in the 2011 and the 2013 IPL. After the 2013 season, PWI owners withdrew from the IPL due to financial differences with the Board of Control for Cricket in India. In total, 46 players had played for PWI, of whom Robin Uthappa had played the most matches (46, since his debut for the franchise in 2011).
The leading run-scorer for PWI was Uthappa, who had scored 1,103 runs. Jesse Ryder scored 86 runs against Delhi Daredevils in 2012, which was the highest individual score in an innings by a PWI batsman. Steve Smith had the team's best batting average: 40.07. Among PWI's bowlers, Rahul Sharma had taken more wickets than any other, claiming 34. The best bowling average among bowlers who had bowled more than 20 overs was Yuvraj Singh's 22.93. Ashok Dinda had the best bowling figures in an innings; he claimed four wickets against Mumbai Indians in a 2012 match, conceding 18 runs. Uthappa had taken the most catches as wicket-keeper for PWI, with 24, and had also made the most stumpings: six. Smith and Manish Pandey had claimed the highest number of catches among fielders, taking 14 each. (Full article...) -
Image 12

Bowlers have taken fifty-three five-wicket hauls in Tests and two five-wicket hauls in One Day International matches played at Chepauk.
M. A. Chidambaram Stadium (MAC), also known as the Chepauk Stadium or simply Chepauk due its location in the city's locality of Chepauk, is a sports ground in Chennai, India that has hosted international cricket matches along with provincial games. Named after M. A. Chidambaram, former President of Board of Control for Cricket in India (BCCI), the venue was formerly known as the Madras Cricket Club ground. It has a capacity of 38,000 spectators for international matches. It is the home ground of the Tamil Nadu cricket team and the Indian Premier League team Chennai Super Kings. The first Test at this venue took place in 1934, between India and England. As of February 2021, it has hosted a further 33 Test matches. Chepauk has also staged 22 One Day International (ODI) matches, the first of which was in 1987 when Australia defeated India in a group-match during the 1987 World Cup.
In cricket, a five-wicket haul (also known as a "five-for" or "fifer") refers to a bowler taking five or more wickets in a single innings. This is regarded as a notable achievement. The first bowler to take a five-wicket haul in a Test match at Chepauk was Amar Singh for India against England in 1934; he finished the innings with bowling figures of 7 wickets for 86 runs. Australia's Ashley Mallett became the first to take two five-wicket hauls in the same match at Chepauk, when he took 5 for 91 and 5 for 53 in the second and fourth innings of the fifth Test of Australia's 1969–70 tour of India. Narendra Hirwani is the most recent cricketer and the first Indian to take two five-wicket hauls on debut. He took 8 for 61 and 8 for 75 against the West Indies during the fourth Test of the 1987–88 series between the teams, which was held at this ground, and finished the match with bowling figures of 16 for 136. These are also the best match-figures by any bowler on Test debut. The best figures in Test cricket at Chepauk are 8 for 55, taken by India's Vinoo Mankad against England in 1952. Axar Patel took the most recent five-wicket haul at Chepauk, with figures of 5 for 60 against England in their 2020–21 tour of India. As of September 2024, 33 bowlers have taken 53 Test match five-wicket hauls at this ground. (Full article...) -
Image 13

The Padma Bhushan is the third-highest civilian award of the Republic of India. Instituted on 2 January 1954, the award is given for "distinguished service of a high order", without distinction of race, occupation, position, or sex. The recipients receive a Sanad, a certificate signed by the President of India and a circular-shaped medallion with no monetary association. The recipients are announced every year on Republic Day (26 January) and registered in The Gazette of India—a publication used for official government notices and released weekly by the Department of Publication, under the Ministry of Urban Development. The conferral of the award is not considered official without its publication in the Gazette. The name of recipient, whose award have been revoked or restored, both of which require the authority of the President, is archived and they are required to surrender their medal when their name is struck from the register; none of the conferments of Padma Bhushan during 1970–1979 have been revoked or restored. The recommendations are received from all the state and the union territory governments, as well as from Ministries of the Government of India, the Bharat Ratna and the Padma Vibhushan awardees, the Institutes of Excellence, the Ministers, the Chief Ministers and the Governors of State, and the Members of Parliament including private individuals.
When instituted in 1954, the Padma Bhushan was classified as "Dusra Varg" (Class II) under the three-tier Padma Vibhushan awards, which were preceded by the Bharat Ratna in hierarchy. On 15 January 1955, the Padma Vibhushan was reclassified into three different awards as the Padma Vibhushan, the Padma Bhushan and the Padma Shri. The criteria included "distinguished service of a high order in any field including service rendered by Government servants", but excluded those working with the public sector undertakings with the exception of doctors and scientists. The 1954 statutes did not allow posthumous awards; this was subsequently modified in the January 1955 statute. The design was also changed to the form that is currently in use; it portrays a circular-shaped toned bronze medallion 1+3⁄4 inches (44 mm) in diameter and 1⁄8 inch (3.2 mm) thick. The centrally placed pattern made of outer lines of a square of 1+3⁄16-inch (30 mm) side is embossed with a knob carved within each of the outer angles of the pattern. A raised circular space of diameter 1+1⁄16 inches (27 mm) is placed at the centre of the decoration. A centrally located lotus flower is embossed on the obverse side of the medal and the text "Padma" is placed above and the text "Bhushan" is placed below the lotus written in Devanagari script. The State Emblem of India is displayed in the centre of the reverse side, together with the national motto of India, "Satyameva Jayate" (Truth alone triumphs) in Devanagari script, which is inscribed on the lower edge. The rim, the edges and all embossing on either side is of standard gold with the text "Padma Bhushan" of gold gilt. The medal is suspended by a pink riband 1+1⁄4 inches (32 mm) in width with a broad white stripe in the middle. It is ranked fifth in the order of precedence of wearing of medals and decorations of the Indian civilian and military awards. (Full article...) -
Image 14

Kapadia at the Pichvai Exhibition in New Delhi, 2018
Dimple Kapadia is an Indian actress who predominantly appears in Hindi films. She was discovered by Raj Kapoor at age 14, who gave her the title role in his teen romance Bobby (1973), opposite his son Rishi Kapoor. The film became a massive commercial success and made her an overnight star. Her role as a Christian teenager from Goa established her as a youth fashion icon and won her the Filmfare Award for Best Actress. Kapadia retired from acting following her marriage to Indian actor Rajesh Khanna earlier in 1973, and returned to the film industry in 1984, after her separation from Khanna. The release of her comeback film, Saagar, was delayed, with Zakhmi Sher becoming the second film of her career. Released in 1985, Saagar earned her a second Best Actress award at Filmfare, and she went on to establish herself as one of the leading actresses of Hindi cinema in the 1980s and early 1990s. The early roles she played following her return included the Hitchcockian thriller Aitbaar (1985), for which she received positive reviews, and the commercially successful action films Arjun (1985) and Janbaaz (1986). During this period, she acted in several films in South India, which she admitted to having made for financial gain and dismissed their quality.
Many of Kapadia's early roles relied on her perceived beauty, and she would struggle to be taken seriously as an actress. She made a decision to accept more serious roles, and won acclaim for her role in the marital drama Kaash (1987). Financial success came with films like Insaniyat Ke Dushman (1987), Insaaf (1987), in which she played double roles; the controversial revenge saga Zakhmi Aurat (1988), in which she played an avenging rape victim; and Ram Lakhan (1989). She started the next decade by venturing into neorealist art films, known in India as parallel cinema, including Drishti (1990), Lekin... (1990), and Rudaali (1993). All these films won her critical praise, and her role as a professional mourner in the latter earned her a National Film Award for Best Actress and a Filmfare Critics Award for Best Actress. She further essayed character parts in Prahaar (1991), Angaar (1992), Gardish (1993), and Krantiveer (1994), which garnered her a fourth Filmfare Award, in the Best Supporting Actress category. (Full article...) -
Image 15
Suriya is an Indian actor and film producer who works primarily in Tamil cinema. He made a commercially successful cinematic debut in Vasanth's Nerrukku Ner (1997). After few critical and commercial failures, Suriya collaborated with Vasanth again in Poovellam Kettuppar (1999), his first film with his future wife Jyothika.
In 2001, Suriya starred in Bala's Nandha as an ex-convict trying to find his place in society. The film was critically acclaimed and became a turning point in his career. His roles as a police officer in Gautham Vasudev Menon's Kaakha Kaakha (which became his first blockbuster) and a con artist in Bala's Pithamagan, established him as one of Tamil cinema's leading actors. Suriya's performances in both films were praised, winning him a Best Actor nomination for the former and the Best Supporting Actor for Pithamagan at the 51st Filmfare Awards South. The following year, he played dual roles—a hunchback and a college student—in Perazhagan. Suriya's performance was again praised, and he received his first Filmfare Best Actor award. He was also acclaimed for his performance as a student leader in Mani Ratnam's Aayutha Ezhuthu (2004). (Full article...) -
Image 16Chopra promoting Golmaal Again in 2017
Parineeti Chopra is an Indian actress who appears in Hindi films. Chopra has 26 awards to her credit including a National Film Award, one each from the Filmfare, Screen and Zee Cine Awards, and two awards each from the Producers Guild and International Indian Film Academy Awards (IIFA).
Chopra made her film debut with a supporting role in the 2011 romantic comedy Ladies vs Ricky Bahl, which won her the Best Female Debut at the 57th Filmfare Awards. She also received Best Debut awards at other ceremonies, including Screen Awards, IIFA Awards, Producers Guild Film Awards, and Zee Cine Awards. Additionally, Chopra won the IIFA Award for Best Supporting Actress, and the Producers Guild Film Award for Best Actress in a Supporting Role, and was nominated in the same category at the Filmfare, Screen, and Zee Cine award ceremonies for her performance in the film. In 2012, she played her first lead role in the action romantic drama Ishaqzaade, for which she earned a Special Mention at the 60th National Film Awards. For the film, Chopra also received her first nomination for the Filmfare Award and Producers Guild Film Award for Best Actress in a Leading Role, among other honours. (Full article...) -
Image 17

Members of the Indian cricket team before a Women's Cricket World Cup game in Sydney
A One Day International (ODI) is an international cricket match between two teams, each having ODI status, as determined by the International Cricket Council. The women's variant of the game is similar to the men's version, with minor modifications to umpiring and pitch requirements. The first women's ODI was played in 1973, between England and Australia. The Indian women's team played their first ever ODI match in 1978, against England, after the Women's Cricket Association of India was formed. The Women's Cricket Association of India was merged with the Board of Control for Cricket in India in 2006 as part of the International Cricket Council's initiative to develop women's cricket.
Since the team was formed, 151 women have represented India in ODI cricket. This list includes all players who have played at least one ODI match and is arranged in the order of debut appearance. Where more than one player won their first cap in the same match, those players are listed alphabetically by last name at the time of debut. (Full article...) -
Image 18The 2022 recipient: Pavan Malhotra
The National Film Award for Best Actor in a Supporting Role (known as National Film Award for Best Supporting Actor prior to 69th NFA) is an honour presented annually at India's National Film Awards ceremony by the National Film Development Corporation of India (NFDC), an organisation set up by the Indian Ministry of Information and Broadcasting. A national panel appointed annually by the NFDC selects the actor who has given the best performance in a supporting role within Indian cinema. The award is presented by the President of India at a ceremony held in New Delhi. Since the 70th National Film Awards, the name was changed to "Best Actor in a Supporting Role".
The winner is given a "Rajat Kamal" (Silver Lotus) certificate and a cash prize of ₹2 lakh (US$2,300). Including ties and repeat winners, the government of India has presented a total of 32 Best Supporting Actor awards to 29 different actors. Although Indian cinema produces films in more than 20 languages, the actors whose performances have won awards have worked in one or more of seven major languages: Hindi (18 awards), Tamil (9 awards), Bengali (3 awards), Malayalam (4 awards), Marathi (3 awards), Telugu (1 award), Kannada (1 award). (Full article...) -
Image 19
Kajol is an Indian actress known for her work in Hindi films. She is a recipient of more than 40 accolades into her credit. Six Filmfare Awards, one Best Performance in a Negative Role for Gupt: The Hidden Truth and record-tying five Best Actress for the romance musicals Dilwale Dulhania Le Jayenge, Kuch Kuch Hota Hai, the family drama Kabhi Khushi Kabhie Gham, the tragedy romantic thriller Fanaa and the social drama My Name Is Khan. In addition to seven nominations. She has received five Screen Awards, four Zee Cine Awards, two Bollywood Movie Award, and one each Stardust Award and Bengal Film Journalists' Association Awards.
Kajol made her acting debut with Bekhudi (1992), and had commercial successes in Baazigar (1993), and Yeh Dillagi (1994). Starring roles in the top-grossing romances Dilwale Dulhania Le Jayenge (1995) and Kuch Kuch Hota Hai (1998) established her as a leading star in the 1990s and earned her two Filmfare Awards for Best Actress.
After making her debut in 1992 with the romance Bekhudi, Kajol received critical acclaim and the Bengal Film Journalists' Association Award for Best Actress for playing an orphaned girl in Udhaar Ki Zindagi (1994). She won her first Filmfare Award for Best Actress for her portrayal of an Indian non-resident in the romantic drama Dilwale Dulhania Le Jayenge (1995), and Best Performance in a Negative Role for her performance as a femme fatale in the psychological thriller Gupt: The Hidden Truth (1997), becoming the first actress to win in the latter category. Additionally, she received the Zee Cine Award for Best Actor – Female for Gupt. (Full article...) -
Image 20

Rahul Dravid during the Australian tour of India in 2004
Rahul Dravid is a retired Indian international cricketer. in both Test and One Day International (ODI) cricket in matches organised by the International Cricket Council (ICC). Nicknamed "The Wall" for his ability of "... fending off the fiercest, the fastest and the wiliest of bowlers around the world", he scored 36 centuries (scores of 100 runs or more) in Test cricket and 12 in One Day Internationals (ODI) between his debut in 1996 and retirement in 2011. He was named as one of the five Wisden Cricketers of the Year in 2000, as well as the ICC Test Player of the Year and ICC Player of the Year in 2004.
Dravid scored his first Test century in January 1997 against South Africa. In a man-of-the-match performance, he made 148 runs spanning nine hours and took India to their only draw of the series. He made centuries in both innings of a match when he scored 190 and 103 not out in the final Test of the 1998–99 series against New Zealand. He repeated the feat in March 2005 when he scored 110 and 135 against Pakistan in another man-of-the-match performance, leading India to victory in the second of the three-match series. Scoring 180 in a fifth-wicket partnership of 376 with VVS Laxman, in the Second Test of the Border-Gavaskar Trophy in 2001, Dravid helped lead India to victory by 171 runs despite being asked to follow-on by the Australians. His partnership with Laxman was the third-highest for the fifth wicket in Test cricket history. Dravid's highest Test score of 270, achieved in April 2004 in Rawalpindi, helped India to an innings victory against Pakistan. The performance was the fourth-highest score by an Indian batsman in Test cricket. He scored centuries against all Test playing nations and was the first cricketer to score centuries in all 10 Test playing nations. (Full article...) -
Image 21

Kapoor at an event in 2013
Karisma Kapoor is an Indian actress widely known for her work in Hindi films. Kapoor made her acting debut at the age of seventeen with the romance Prem Qaidi in 1991, which was a box office hit. She then appeared in successful ventures, drama Sapne Sajan Ke (1992), and action drama Jigar (1992). Kapoor had her first commercial success in a leading role in romantic action drama Anari (1993), which was a moderate success and was one of the highest-grossing Hindi films of 1993. Between 1993–1996 she featured in several highly successful films, including the comedy drama Raja Babu (1994), action drama Suhaag (1994), action comedy Andaz (1994), the comedies Coolie No. 1 (1995), Saajan Chale Sasural (1996), and Hero No. 1 (1997), and the action thriller Jeet (1996). The success of these films marked a turning point in her career, and established Kapoor as one of the leading actresses in Hindi cinema.
Kapoor's career prospects improved in 1996 when Dharmesh Darshan cast her in his romantic drama Raja Hindustani. With worldwide earnings of ₹763.4 million (US$8.8 million), it emerged as the highest-grossing film of the year and the fourth highest-grossing film in India of the 1990s. The film earned her praise from critics, and Kapoor won her first Filmfare Award for Best Actress. The following year, she received widespread recognition as well as the National Film Award and Filmfare Award for Best Supporting Actress for portraying a headstrong dancer in Dil To Pagal Hai, a musical romantic drama produced by Yash Raj Films. Subsequently, she played leading roles in several blockbuster films, including the comedies Biwi No.1 (1999), the ensemble family drama Hum Saath-Saath Hain (1999), and the romantic comedy Dulhan Hum Le Jayenge (2000). Her acclaimed performance of a disillusioned sister of Hrithik Roshan's character in the crime drama Fiza (2000) which earned her a second Best Actress award at Filmfare. The following year, she portrayed actress Zubeida Begum in the biographical drama Zubeidaa (2001), won her a Filmfare Award for Best Actress (Critics). In 2002, she portrayed a troubled daughter-in-law in the revenge-seeking war drama Shakti: The Power. (Full article...) -
Image 22

Bajirao Mastani won a total of seven National Film Awards at the 63rd National Film Awards including the National Film Award for Best Direction for Sanjay Leela Bhansali.
Bajirao Mastani is a 2015 Indian epic historical romance film directed and scored by Sanjay Leela Bhansali. It was a co-production between Bhansali Productions and Eros International. The film stars Ranveer Singh as Bajirao I, Deepika Padukone as Mastani, and Priyanka Chopra as Kashibai. Tanvi Azmi, Aditya Pancholi, Vaibbhav Tatwawdi and Milind Soman playing supporting roles. The screenplay was written by Prakash R. Kapadia, and the cinematography provided by Sudeep Chatterjee. Based on the Marathi novel Raau by Nagnath S. Inamdar, the film narrates the story of the Maratha Peshwa Bajirao and his second wife Mastani.
Made on a budget of ₹1.25 billion (US$14 million), the film was released on 18 December 2015 to positive reviews from critics. As of May 2016, Bajirao Mastani has grossed over ₹3.6 billion (US$42 million) at the box-office, becoming one of the highest-grossing Indian films of all time. The film garnered awards and nominations in a variety of categories with particular praise for Bhansali's direction and music, the performances of Chopra and Singh, its cinematography, art direction, and costume design. (Full article...) -
Image 23
Tamannaah Bhatia is an Indian actress known for her work in Telugu, Tamil and Hindi cinema. She debuted as a leading lady in the Hindi film Chand Sa Roshan Chehra in 2005. That same year marked her Telugu debut with Sree, followed by her Tamil debut in Kedi the subsequent year. She experienced a breakthrough in her career with the success of Happy Days and Kalloori in 2007, portraying college students in both films. Her journey continued with box-office hits like Ayan, 100% Love, Siruthai, Tadakha, Oosaravelli, Racha and Veeram as well as setbacks such as Ananda Thandavam, Endukante Premanta, Himmatwala, Humshakals and Aagadu. Additionally, while she received critical acclaim and several accolades for her role in 100% Love, her performances in Himmatwala and Humshakals faced criticism.
In 2015, Bhatia received praised for her role in Baahubali: The Beginning, which earned over ₹600 crore. She was praised for her performances in Oopiri and Dharma Durai, and her double role in Devi was well received. However, Vasuvum Saravananum Onna Padichavanga, Bengal Tiger and Kaththi Sandai were less successful. In 2017, she reprised her role in Baahubali 2: The Conclusion, which grossed over ₹1700 crore worldwide, while Anbanavan Asaradhavan Adangadhavan was a box office failure. In 2018, Sketch received mixed reviews, but her performance was praised, while Naa Nuvve and Next Enti? were poorly received. In 2019, she starred in the blockbuster F2: Fun and Frustration and delivered notable performances in Kanne Kalaimaane, Devi 2, Khamoshi, Sye Raa Narasimha Reddy and Petromax. (Full article...) -
Image 24

The Padma Bhushan is the third-highest civilian award of the Republic of India. Instituted on 2 January 1954, the award is given for "distinguished service of a high order", without distinction of race, occupation, position, or sex. The recipients receive a Sanad, a certificate signed by the President of India and a circular-shaped medallion with no monetary association. The recipients are announced every year on Republic Day (26 January) and registered in The Gazette of India—a publication used for official government notices and released weekly by the Department of Publication, under the Ministry of Urban Development. The conferral of the award is not considered official without its publication in the Gazette. The name of a recipient, whose award has been revoked or restored, both of which require the authority of the President, is archived and they are required to surrender their medal when their name is struck from the register. As of 2019[update], none of the conferments of Padma Bhushan during the 2010s have been revoked or restored. The recommendations are received from all the state and the union territory governments, as well as from Ministries of the Government of India, the Bharat Ratna and the Padma Vibhushan awardees, the Institutes of Excellence, the Ministers, the Chief Ministers and the Governors of State, and the Members of Parliament including private individuals.
When instituted in 1954, the Padma Bhushan was classified as "Dusra Varg" (Class II) under the three-tier Padma Vibhushan awards, which were preceded by the Bharat Ratna in hierarchy. On 15 January 1955, the Padma Vibhushan was reclassified into three different awards as the Padma Vibhushan, the Padma Bhushan and the Padma Shri. The criteria included "distinguished service of a high order in any field including service rendered by Government servants", but excluded those working with the public sector undertakings with the exception of doctors and scientists. The 1954 statutes did not allow posthumous awards; this was subsequently modified in the January 1955 statute. The design was also changed to the form that is currently in use; it portrays a circular-shaped toned bronze medallion 1+3⁄4 inches (44 mm) in diameter and 1⁄8 inch (3.2 mm) thick. The centrally placed pattern made of outer lines of a square of 1+3⁄16 inches (30 mm) side is embossed with a knob carved within each of the outer angles of the pattern. A raised circular space of diameter 1+1⁄16 inches (27 mm) is placed at the centre of the decoration. A centrally located lotus flower is embossed on the obverse side of the medal and the text "Padma" is placed above and the text "Bhushan" is placed below the lotus written in Devanagari script. The State Emblem of India is displayed in the centre of the reverse side, together with the national motto of India, "Satyameva Jayate" (Truth alone triumphs) in Devanagari script, which is inscribed on the lower edge. The rim, the edges and all embossing on either side is of standard gold with the text "Padma Bhushan" of gold gilt. The medal is suspended by a pink riband 1+1⁄4 inches (32 mm) in width with a broad white stripe in the middle. It is ranked fifth in the order of precedence of wearing of medals and decorations of the Indian civilian and military awards. (Full article...) -
Image 25Padmaavat is a 2018 Indian Hindi-language epic period drama film directed and produced by Sanjay Leela Bhansali. The film stars Deepika Padukone as Rani Padmavati, Shahid Kapoor as Maharawal Ratan Singh and Ranveer Singh as Sultan Alauddin Khilji and features Aditi Rao Hydari, Jim Sarbh, Raza Murad, and Anupriya Goenka in supporting roles. The film's screenplay was written by Bhansali and Prakash Kapadia. Bhansali also composed the soundtrack of the film, with lyrics written by A. M. Turaz, Siddharth-Garima and Swaroop Khan. The original score of the film is composed by Sanchit Balhara. Padmaavat was edited by Rajesh G. Pandey while Sudeep Chatterjee is its cinematographer. Set in medieval Rajasthan in 1303 AD, Queen Padmavati of Mewar is married to a noble king and they live in a prosperous fortress with their subjects until an ambitious Sultan hears of Padmavati's beauty and becomes obsessed with having her.
Made on a budget of ₹2.15 billion (US$25 million), Padmaavat was released on 25 January 2018 in 2D, 3D and IMAX 3D formats, making it the first Indian film to be released in IMAX 3D. Despite not being released in some states of India, it grossed over ₹5.85 billion (US$68 million) at the box office, becoming a commercial success and one of the highest-grossing Indian films of all time. The film won 25 awards from 68 nominations; its music, and the performance of Singh have received the most attention from award groups. (Full article...)
 Good article – show another
Good article – show another
-
Image 1Painting depicting Varaha by Raja Ravi Varma, circa 1930
Varaha (Sanskrit: वराह, Varāha, "boar") is the avatara of the Hindu god Vishnu, in the form of a boar. Varaha is generally listed as third in the Dashavatara, the ten principal avataras of Vishnu.
Varaha lifts the earth goddess Bhumi out of the cosmic ocean when the demon Hiranyaksha stole the earth goddess and hid her in the primordial waters, Vishnu appeared as Varaha to rescue her. Varaha killed Hiranyaksha and retrieved the earth goddess from the cosmic ocean, lifting it on his tusks, and restored her to her place in the universe. (Full article...) -
Image 2
Mahendra Singh Dhoni (/məˈheɪndrə ˈsɪŋ dhæˈnɪ/ ⓘ; born 7 July 1981) is an Indian professional cricketer who plays as a right-handed batter and a wicket-keeper. Widely regarded as one of the most prolific wicket-keeper batsmen and captains, he represented the Indian cricket team and was the captain of the side in limited overs formats from 2007 to 2017 and in test cricket from 2008 to 2014. Dhoni has captained the most international matches and is the most successful Indian captain. He has led India to victory in the 2007 ICC World Twenty20, the 2011 Cricket World Cup, and the 2013 ICC Champions Trophy, being the only captain to win three different limited overs ICC tournaments. He also led the teams that won the Asia Cup in 2010, 2016 and was a member of the title winning squad in 2018.
Born in Ranchi, Dhoni made his first class debut for Bihar in 1999. He made his debut for the Indian cricket team on 23 December 2004 in an ODI against Bangladesh and played his first test a year later against Sri Lanka. In 2007, he became the captain of the ODI side before taking over in all formats by 2008. Dhoni retired from test cricket in 2014 but continued playing in limited overs cricket till 2019. He has scored 17,266 runs in international cricket including 10,000 plus runs at an average of more than 50 in ODIs. (Full article...) -
Image 3
Fort Dansborg (Danish: Dansborg), locally called Danish Fort, is a Danish fort located in the shores of Bay of Bengal in Tranquebar (Tharangambadi) in the South Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Fort Dansborg was built in the land ceded by Thanjavur king Ragunatha Nayak in an agreement with Danish Admiral Ove Gjedde in 1620 and acted as the base for Danish settlement in the region during the early 17th century. The fort is the second largest Danish fort after Kronborg. The fort was sold to the British in 1845 and along with Tranquebar, the fort lost its significance as the town was not an active trading post for the British. After India's independence in 1947, the fort was used as an inspection bungalow by the state government until 1978 when its archaeology department took control of the fort. The fort is now used as a museum where the major artifacts of the fort and the Danish colonial empire in India are displayed.
The fort was renovated twice in modern times, by the Tranquebar Association with the help of the Danish royal family and the state's archaeology department in 2001 and by the state's tourism department in 2011. (Full article...) -
Image 4The Jungle Book is a 1967 American animated musical adventure film produced by Walt Disney Productions and released by Buena Vista Distribution. Based very loosely on the "Mowgli" stories from Rudyard Kipling's 1894 book of the same name, it is the final animated feature film to be produced by Walt Disney, who died during its production. It was directed by Wolfgang Reitherman and written by Larry Clemmons, Ralph Wright, Ken Anderson, and Vance Gerry. Featuring the voices of Phil Harris, Sebastian Cabot, Louis Prima, George Sanders, and Sterling Holloway, the film's plot follows Mowgli, a feral child raised in the Indian jungle by wolves, as his friends, Bagheera the panther and Baloo the bear, try to convince him to leave the jungle before the ruthless tiger Shere Khan arrives.
The early versions of both the screenplay and the soundtrack followed Kipling's work more closely, with a dramatic, dark, and sinister tone, which Disney did not want in his family film, leading to writer Bill Peet and songwriter Terry Gilkyson being replaced. (Full article...) -
Image 5
Verghese Kurien (26 November 1921 – 9 September 2012) was an Indian dairy engineer and social entrepreneur. He led initiatives that contributed to the extensive increase in milk production in India termed as the White Revolution.
Kurien graduated in physics from the University of Madras in 1940 and received his masters in mechanical engineering from the Michigan State University in 1947. In 1949, Kurien was sent by the Government of India to run its experimental creamery at Anand, where he set up the Kaira District Cooperative Milk Producers' Union in 1950 which later became Amul. Amul organised the dairy farmers in the villages as a part of cooperatives and linked them to the milk consumers directly. (Full article...) -
Image 6The Param Vir Chakra (PVC) is India's highest military decoration, awarded for displaying distinguished acts of valour during wartime. Param Vir Chakra translates as the "Wheel of the Ultimate Brave", and the award is granted for "most conspicuous bravery in the presence of the enemy". As of January 2018[update], the medal has been awarded 21 times, of which 14 were posthumous and 16 arose from actions in Indo-Pakistani conflicts. Of the 21 awardees, 20 have been from the Indian Army and one has been from the Indian Air Force. Major Somnath Sharma was the first recipient. A number of state governments of India as well as ministries of the central government provide allowances and rewards to recipients of the PVC (or their family members in case of the recipient's death).
The history of present-day Indian gallantry awards can be traced back to the rule of the East India Company, when the first formal award was instituted by Lord William Bentinck in 1834 as the Order of Merit, later renamed the Indian Order of Merit in 1902. During the First World War, the British awards system was adopted and continued through the Second World War. Post-independence, new awards were instituted on 26 January 1950, with retroactive effect from 15 August 1947. The PVC is equivalent to the Victoria Cross in the United Kingdom and the Medal of Honor in the United States. (Full article...) -
Image 7

There Comes Papa is an 1893 painting by the Indian artist Raja Ravi Varma. The painting focuses on Varma's daughter (Mahaprabha Thampuratty) and grandson (Marthanda Varma), looking towards the left at an approaching father. Evoking both Indian and European style, the painting has been noted by critics for its symbolism regarding of the Nair matrilineal practices. (Full article...) -
Image 8Guru Sishyan (pronounced [ɡuɾu siʂjan] transl. Master and Disciple) is a 1988 Indian Tamil-language action comedy film directed by S. P. Muthuraman. A remake of the Hindi film Insaf Ki Pukar (1987), it stars Rajinikanth, Prabhu, Seetha and Gautami with Pandiyan, Cho Ramaswamy, Ravichandran, Radha Ravi, Senthamarai, Vinu Chakravarthy and Manorama in supporting roles. The film is about two ex-convicts who set out to prove the innocence of their wrongfully imprisoned fellow convict.
Meena Panchu Arunachalam produced Guru Sishyan under the production company P. A. Art Productions. The screenplay was written by her husband Panchu Arunachalam. The cinematography was handled by T. S. Vinayagam, the editing was by R. Vittal and C. Lancy, and the art direction was by B. Chalam. The film is Gautami's debut role in Tamil cinema, and the first film in which Rajinikanth and Prabhu co-starred. Filming took place primarily in Mysore and Chennai, and was completed in 25 days. (Full article...) -
Image 9
The Devi Upanishad (Sanskrit:देवी उपनिषत्), is one of the minor Upanishads of Hinduism and a text composed in Sanskrit. It is one of the 19 Upanishads attached to the Atharvaveda, and is classified as one of the eight Shakta Upanishads. It is, as an Upanishad, a part of the corpus of Vedanta literature collection that present the philosophical concepts of Hinduism.
The text was likely composed between 9th- to 14th-centuries CE. It refers to Mahadevi as representing all goddesses. The Devi Upanishad is part of the five Atharvashiras Upanishads important to Tantra and Shakta philosophy traditions. (Full article...) -
Image 10Lieutenant Colonel Ardeshir Burzorji Tarapore, PVC (18 August 1923 – 16 September 1965), was an Indian military officer and posthumous recipient of India's highest military award, the Param Vir Chakra. After completing his schooling in Pune, Tarapore joined the Hyderabad Army, and was commissioned in January 1942. Initially he joined the infantry, but was later transferred to an armoured regiment, the 1st Hyderabad Imperial Service Lancers. During World War II, Tarapore saw action in the Middle Eastern theatre of the war.
After Hyderabad State was annexed by India in 1948, Tarapore was selected to join the Indian Army. He was commissioned again in April 1951, and was posted to the Poona Horse regiment, 17th Battalion. Later he attended a training course in the United Kingdom on the Centurion tank. During the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965, 17 Horse saw action in the Sialkot sector. Tarapore led the regiment in several tank battles between 11 and 16 September, and was killed in one such battle at Butur-Dograndi on 16 September. Under his leadership the regiment destroyed sixty Pakistani tanks, while the Indians suffered the loss of nine. (Full article...) -
Image 11Chandramukhi (transl. Moon-faced lady) is a 2005 Indian Tamil-language psychological horror comedy film written and directed by P. Vasu. It is a remake of Vasu's Kannada film Apthamitra (2004) which itself was remake of Malayalam film Manichitrathazhu (1993). The film stars Rajinikanth, Prabhu and Jyothika along with an ensemble supporting cast, including Vadivelu, Nayanthara, Nassar and Sheela. It revolves around a woman who suffers from dissociative identity disorder that affects a family, and a psychiatrist who intends to solve the case while risking his life.
Chandramukhi was produced by Prabhu and his brother Ramkumar Ganesan through their company Sivaji Productions, and is the company's 50th film. The soundtrack album and background score were composed by Vidyasagar. Cinematography was handled by Sekhar V. Joseph and editing was done by Suresh Urs. Principal photography began on 24 October 2004 and was completed in March 2005. (Full article...) -
Image 12

The Bugun liocichla (Liocichla bugunorum) is a passerine bird species from the family Leiothrichidae closely related to the Emei Shan liocichla. First spotted in 1995 in Arunachal Pradesh, India, it was described as a new species in 2006. The description was made without the collection of a type specimen as they were too few to risk killing one. It is thought to be an endangered species, with a small population, and a very restricted distribution range within which commercial development threatens the habitat. (Full article...) -
Image 13AK vs AK is a 2020 Indian Hindi-language black comedy thriller film directed by Vikramaditya Motwane and is the first release under his banner Andolan Films. Anurag Kashyap, the executive producer and dialogue writer, also stars alongside Anil Kapoor as the title characters with Harshvardhan Kapoor and debutante Yogita Bihani in pivotal roles.
The story, written by Avinash Sampath, utilises a film-within-a-film narrative where the main actors play fictionalised versions of themselves. After a public feud between Kashyap, an eccentric film director, and Anil Kapoor, an ageing film star, the former kidnaps the latter's daughter (Sonam Kapoor Ahuja) and forces Kapoor to search for her while his assistant (Bihani) films them as part of his next project, with most of the film shown from the perspective of her camera. (Full article...) -
Image 14Kadhalikka Neramillai (transl. No Time for Love) is a 1964 Indian Tamil-language romantic comedy film produced and directed by C. V. Sridhar, who also conceived and co-wrote its script with Chitralaya Gopu. The film features an ensemble cast consisting of Balaiah, Muthuraman, Nagesh, Rajasree, Sachu, Ravichandran and Kanchana. The latter two made their acting debut with this film.
The plot of Kadhalikka Neramillai revolves around Viswanathan, an estate owner who hopes to get his daughters Nirmala and Kanchana married to wealthy grooms. However, Nirmala falls in love with Ashok, a poor man who was once employed by Vishwanathan. To earn Viswanathan's approval, Ashok pretends to be the only heir of a rich businessman; he is supported by his friend Vasu, who poses as Ashok's fictional millionaire father Chidambaram. A comedy of errors ensues when Vasu discovers his lover Kanchana is Viswanathan's other daughter. (Full article...) -
Image 15The East Bengal Ultras (Bengali pronunciation: [ˈi:st ˌbenˈɡɔːl ˈʌltrəz]) is the vocal supporters' group of an Indian football club, East Bengal, which competes in the ISL—the top tier football league in India. The group is also often referred to as the Bangal Brigade since much of its fanbase originates from the eastern region of Bengal. Founded in 2013, it was the first Ultras group in Indian football and has been credited with revolutionising the Indian football fan movement. East Bengal Ultras was the first supporters' group in India to organise an on-field pyrotechnics show and the first in South Asia to organise a live chant show, which was named Tunes of Colony, in 2019. The group has around 25 chants and slogans.
East Bengal Ultras is known for making some of the largest unique tifos in Indian football. In the 2019–20 I-League season, it set a record for the biggest tifo—10,000 sq ft (930 m2)—in Indian football history at that time, breaking the previous record of 7,200 sq ft (670 m2) which the group had also set. (Full article...) -
Image 16
Alimuddin (Urdu: علیم الدین; 15 December 1930 – 12 July 2012) was a Pakistani cricketer who played 25 Tests for Pakistan between 1954 and 1962. His name is sometimes rendered Alim-ud-Din. A fast-scoring, right-handed opening batsman and occasional right-arm leg break bowler, he was the youngest player ever to appear in first-class cricket, aged 12 years and 73 days. In international cricket, he scored 1,091 runs at the average of 25.37, including two centuries and seven fifties. In 1954, he was a member of the Pakistani squad which toured England and recorded Pakistan's first Test match win. Former Pakistani captain Mushtaq Mohammad said about him that he was "a thorough gentleman as well as a great cricketer for Pakistan". (Full article...) -
Image 17Statue of Shiva at Shivoham Shiva Temple, Bangalore, Karnataka
Shiva (/ˈʃɪvə/; Sanskrit: शिव, lit. 'The Auspicious One', IAST: Śiva [ɕɪʋɐ]), also known as Mahadeva (/məˈhɑː ˈdeɪvə/; Sanskrit: महादेव:, lit. 'The Great God', IAST: Mahādevaḥ, [mɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh]) or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hinduism.
Shiva is known as The Destroyer within the Trimurti, the Hindu trinity which also includes Brahma and Vishnu. In the Shaivite tradition, Shiva is the Supreme Lord who creates, protects and transforms the universe. In the goddess-oriented Shakta tradition, the Supreme Goddess (Devi) is regarded as the energy and creative power (Shakti) and the equal complementary partner of Shiva. Shiva is one of the five equivalent deities in Panchayatana puja of the Smarta tradition of Hinduism. (Full article...) -
Image 18

Mumbai (/mʊmˈbaɪ/ muum-BY; ISO: Muṁbaī, Marathi: [ˈmumbəi] ⓘ), also known as Bombay (/bɒmˈbeɪ/ bom-BAY; its official name until 1995), is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Mumbai is the financial capital and the most populous city proper of India with an estimated population of 12.5 million (1.25 crore). Mumbai is the centre of the Mumbai Metropolitan Region, the sixth-most populous metropolitan area in the world with a population of over 23 million (2.3 crore). Mumbai lies on the Konkan coast on the west coast of India and has a deep natural harbour. In 2008, Mumbai was named an alpha world city. Mumbai has the highest number of billionaires out of any city in Asia.
The seven islands that constitute Mumbai were earlier home to communities of Marathi language-speaking Koli people. For centuries, the seven islands of Bombay were under the control of successive indigenous rulers before being ceded to the Portuguese Empire, and subsequently to the East India Company in 1661, through the dowry of Catherine Braganza when she was married off to Charles II of England. Beginning in 1782, Mumbai was reshaped by the Hornby Vellard project, which undertook reclamation of the area between the seven islands from the Arabian Sea. Along with the construction of major roads and railways, the reclamation project, completed in 1845, transformed Mumbai into a major seaport on the Arabian Sea. Mumbai in the 19th century was characterised by economic and educational development. During the early 20th century it became a strong base for the Indian independence movement. Upon India's independence in 1947 the city was incorporated into Bombay State. In 1960, following the Samyukta Maharashtra Movement, a new state of Maharashtra was created with Mumbai as the capital. (Full article...) -
Image 19Matsya avatar in British Museum, 1820
Matsya (Sanskrit: मत्स्य, lit. 'fish') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya may be depicted as a giant fish, often golden in color, or anthropomorphically with the torso of Vishnu connected to the rear half of a fish.
The earliest account of Matsya is found in the Shatapatha Brahmana, where Matsya is not associated with any particular deity. The fish-saviour later merges with the identity of Brahma in post-Vedic era, and still later, becomes regarded with Vishnu. The legends associated with Matsya expand, evolve, and vary in Hindu texts. These legends have embedded symbolism, where a small fish with Manu's protection grows to become a big fish, and the fish saves the man who would be the progenitor of the next race of mankind. In later versions, Matsya slays a demon named Hayagriva who steals the Vedas, and thus is lauded as the saviour of the scriptures. (Full article...) -
Image 20

Gujarati cinema, also known as Dhollywood, is the segment of Indian cinema, dedicated to the production of motion pictures in the Gujarati language widely spoken in the state of Gujarat. It is based in Ahmedabad. It is one of the major regional and vernacular film industries of the cinema of India, having produced more than one thousand films since its inception.
During the silent film era, many individuals in the industry were Gujaratis. The language-associated industry dates back to 1932, when the first Gujarati talkie, Narsinh Mehta, was released. Until the independence of India in 1947, only twelve Gujarati films were produced. There was a spurt in film production in the 1940s focused on saint, sati or dacoit stories as well as mythology and folktales. In the 1950s–1960s, the trend continued with the addition of films on literary works. In the 1970s, the Government of Gujarat announced a tax exemption and subsidies which resulted in an increase in the number of films, but the quality declined. (Full article...) -
Image 21Painting of Adi Shankara, exponent of Advaita Vedanta with his disciples by Raja Ravi Varma
Adi Shankara (8th c. CE), also called Adi Shankaracharya (Sanskrit: आदि शङ्कर, आदि शङ्कराचार्य, romanized: Ādi Śaṅkara, Ādi Śaṅkarācārya, lit. 'First Shankaracharya', pronounced [aːd̪i ɕɐŋkɐraːt͡ɕaːrjɐ]), was an Indian Vedic scholar, philosopher and teacher (acharya) of Advaita Vedanta. Reliable information on Shankara's actual life is scanty, and his true impact lies in his "iconic representation of Hindu religion and culture," despite the fact that most Hindus do not adhere to Advaita Vedanta. He is seen by Hindus as "the one who restored the Hindu dharma against the attacks of the Buddhists (and Jains) and in the process helped to drive Buddhism out of India." Tradition also portrays him as the one who reconciled the various sects (Vaishnavism, Shaivism, and Saktism) with the introduction of the Pañcāyatana form of worship, the simultaneous worship of five deities – Ganesha, Surya, Vishnu, Shiva and Devi, arguing that all deities were but different forms of the one Brahman, the invisible Supreme Being.
While often revered as the most important Indian philosopher, the historical influence of his works on Hindu intellectual thought has been questioned. Until the 10th century Shankara was overshadowed by his older contemporary Maṇḍana Miśra, and there is no mention of him in concurring Hindu, Buddhist or Jain sources until the 11th century. The popular image of Shankara started to take shape in the 14th century, centuries after his death, when Sringeri matha started to receive patronage from the kings of the Vijayanagara Empire and shifted their allegiance from Advaitic Agamic Shaivism to Brahmanical Advaita orthodoxy. Hagiographies dating from the 14th-17th centuries deified him as a ruler-renunciate, travelling on a digvijaya (conquest of the four quarters) across the Indian subcontinent to propagate his philosophy, defeating his opponents in theological debates. These hagiographies portray him as founding four mathas ("monasteries"), and Adi Shankara also came to be regarded as the organiser of the Dashanami monastic order, and the unifier of the Shanmata tradition of worship. The title of Shankaracharya, used by heads of certain monasteries in India, is derived from his name. (Full article...) -
Image 22
Atal Bihari Vajpayee (25 December 1924 – 16 August 2018) was an Indian politician, poet, and statesman who served as the prime minister of India, first for a term of 13 days in 1996, then for a period of 13 months from 1998 to 1999, followed by a full term from 1999 to 2004. He was the first non-Congress prime minister to serve a full term in the office. Vajpayee was one of the co-founders and a senior leader of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP). He was a member of the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), a Hindu nationalist paramilitary volunteer organisation. He was also a Hindi poet and a writer.
He was a member of the Indian Parliament for over five decades, having been elected ten times to the Lok Sabha, the lower house, and twice to the Rajya Sabha, the upper house. He served as the Member of Parliament from Lucknow, Gwalior, New Delhi and Balrampur constituencies, before retiring from active politics in 2009 due to health concerns. He was among the founding members of the Bharatiya Jana Sangh (BJS), of which he was president from 1968 to 1972. The BJS merged with several other parties to form the Janata Party, which won the 1977 general election. In March 1977, Vajpayee became the Minister of External Affairs in the cabinet of Prime Minister Morarji Desai. He resigned in 1979, and the Janata alliance collapsed soon after. Former members of the Bharatiya Jana Sangh formed the BJP in 1980, with Vajpayee as its first president. (Full article...) -
Image 23

Leslie Simon Goonewardene (Sinhala: ලෙස්ලි සයිමන් ගුනවර්ධන, Tamil: லெஸ்லி சைமன் குணவர்தன; 31 October 1909 – 11 April 1983) was a prominent Sri Lankan statesman. He founded Sri Lanka's first political party, the Lanka Sama Samaja Party, in 1935, and served as its General-Secretary from 1935 to 1977. Goonewardene was a key figure in both the Indian independence movement and the Sri Lankan independence movement. He was designated as a National Hero of Sri Lanka for his leadership in the independence movement, and his efforts are celebrated each year on the Sri Lankan Independence Day.
Born into an aristocratic Panaduran family, Goonewardene was brought up Methodist, educated in English-medium schools, and spoke Sinhala as well as English. Goonewardene was shaped by the widespread Marxist teachings of the time, notably conflicting with his own privilege, resulting in him pursuing the study of government from the London School of Economics. There, he was deeply influenced by the teachings of his professor, Harold Laski. Upon his return to Ceylon from London, Goonewardene founded the Lanka Sama Samaja Party in 1935. He rose to prominence leading the party through World War II, when it was key to the anti-war movement, culminating in its proscription and his escape from Ceylon to India. (Full article...) -
Image 24
The Salt march, also known as the Salt Satyagraha, Dandi March, and the Dandi Satyagraha, was an act of nonviolent civil disobedience in colonial India, led by Mahatma Gandhi. The 24-day march lasted from 12 March 1930 to 6 April 1930 as a direct action campaign of tax resistance and nonviolent protest against the British salt monopoly. Another reason for this march was that the Civil Disobedience Movement needed a strong inauguration that would inspire more people to follow Gandhi's example. Gandhi started this march with 78 of his trusted volunteers. The march spanned 387 kilometres (240 mi), from Sabarmati Ashram to Dandi, which was called Navsari at that time (now in the state of Gujarat). Growing numbers of Indians joined them along the way. When Gandhi broke the British Raj salt laws at 8:30 am on 6 April 1930, it sparked large-scale acts of civil disobedience against the salt laws by millions of Indians.
After making the salt by evaporation at Dandi, Gandhi continued southward along the coast, making salt and addressing meetings on the way. The Congress Party planned to stage a satyagraha at the Dharasana Salt Works, 40 km (25 mi) south of Dandi. However, Gandhi was arrested on the midnight of 4–5 May 1930, just days before the planned action at Dharasana. The Dandi March and the ensuing Dharasana Satyagraha drew worldwide attention to the Indian independence movement through extensive newspaper and newsreel coverage. The satyagraha against the salt tax continued for almost a year, ending with Gandhi's release from jail and negotiations with Viceroy Lord Irwin at the Second Round Table Conference. Although over 60,000 Indians were jailed as a result of the Salt Satyagraha, the British did not make immediate major concessions. (Full article...) -
Image 25"Within You Without You" is a song by the English rock band the Beatles from their 1967 album Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band. Written by lead guitarist George Harrison, it was his second composition in the Indian classical style, after "Love You To", and inspired by his stay in India in late 1966 with his mentor and sitar teacher Ravi Shankar. Recorded in London without the other Beatles, it features Indian instrumentation such as sitar, tambura, dilruba and tabla, and was performed by Harrison and members of the Asian Music Circle. The recording marked a significant departure from the Beatles' previous work; musically, it evokes the Indian devotional tradition, while the overtly spiritual quality of the lyrics reflects Harrison's absorption in Hindu philosophy and the teachings of the Vedas.
The song was Harrison's only composition on Sgt. Pepper, although his endorsement of Indian culture was further reflected in the inclusion of yogis such as Paramahansa Yogananda among the crowd depicted on the album's cover. With the worldwide success of the album, "Within You Without You" presented Indian classical music to a new audience in the West and contributed to the genre's peak in international popularity. It also influenced the philosophical direction of many of Harrison's peers during an era of utopian idealism marked by the Summer of Love. The song has traditionally received a varied response from music critics, some of whom find it lacklustre and pretentious, while others admire its musical authenticity and consider its message to be the most meaningful on Sgt. Pepper. Writing for Rolling Stone, David Fricke described the track as "at once beautiful and severe, a magnetic sermon about materialism and communal responsibility in the middle of a record devoted to gentle Technicolor anarchy". (Full article...)
News
- 9 February 2025 – Naxalite–Maoist insurgency
- Thirty-one Maoist militants and two security forces are killed during a shootout around Indravati River in Chhattisgarh, India. (Al Jazeera)
- 7 February 2025 –
- German Federal Police detains 16 Indian nationals found in a van in Aachen, North Rhine-Westphalia, including 15 passengers and the driver, as they attempt to enter the country without valid documents. (DW)
- 29 January 2025 – 2025 Prayag Kumbh Mela
- At least 30 people are killed in a crowd crush at a Hindu festival in Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh, India. (BBC News)
- 29 January 2025 – 2025 Light Air Services Beechcraft 1900 crash
- A Beechcraft 1900D carrying employees of an oil company crashes in Unity, South Sudan, killing 20 of the 21 people onboard, including one Indian and two Chinese nationals. (CNN) (Reuters)
- 27 January 2025 – China–India relations
- Following the meeting between Indian Foreign Secretary Vikram Misri and Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi in Beijing, China and India agree to resume direct air travel between the two countries after a five-year hiatus. (CNA).
Did you know...
- ... that the 2022 Yangtse clash saw Chinese and Indian troops fight hand-to-hand with melee weapons on a high-elevation ridgeline that formed their frontier in the area?
- ... that poor aircraft maintenance practices contributed to the crash of Indian Airlines Flight 503?
- ... that in the 1932 baseball game in which pitcher Eddie Rommel won his last game, he pitched 17 innings in relief, an American League record?
- ... that the restoration of Neknampur Lake was recognised "as the best model of lake restoration in India"?
- ... that after becoming a religious leader of the Upper Skagit Indian Tribe, Slaybebtikud united the tribes and established himself as their sole leader?
- ... that Arthur France founded the Leeds West Indian Carnival, the first Caribbean carnival in Europe, in 1967?
Topics related to India
Timeline of Indian history, Indus Valley Civilisation, Dholavira, Science and technology in ancient India, Meluhha, Aryan invasion theory, Out of India theory, Greek conquests in India, Indian maritime history, Maurya Empire, Ashoka, Shunga Empire, Hoysala Empire, Vijayanagara, Satavahana dynasty, Indo-Greek Kingdom, Indo-Scythians, Indo-Parthian Kingdom, Kushan Empire, Western Satraps, Gupta Empire, Chola dynasty, Pala Empire, Islamic incursions in India, Mughal Empire, Maratha Empire, British Raj, East India Company, Governor-General, Viceroy, War of Independence, 1857, Indian independence movement, Indian National Army, Azad Hind, Quit India Movement, Partition of India, History of Republic of India, Non-Aligned Movement, Sino-Indian War, Indo-Pakistani War of 1947–1948, Indo-Pakistani War of 1965, Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, Kargil War, 2001–02 India–Pakistan standoff, Military, Demographic
Law, Hindu law, Constitution, Political parties (Indian National Congress, Bharatiya Janata Party), Foreign relations, Elections, Political divisions, Reservation in India
Government agencies, Legislative branch (Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha) Executive branch (President & Vice President, Prime Minister & Deputy Prime Minister, Cabinet Ministers, Cabinet Secretary, Election Commission, Foreign Minister; Law enforcement: CBI, CID, Intelligence: IB, RAW), Directorate General of Income Tax Investigation Judicial branch (Supreme Court), Armed Forces (Army, Navy, Air Force, Border Security Force, Coast Guard)
Himalayas, Western Ghats, Eastern Ghats, Indo-Gangetic Plain, Deccan Plateau, Thar Desert, Ganges, Rann of Kutch, Brahmaputra River, Northeast India; Mountains, Valleys, Islands, Rivers; States and union territories, Cities, Districts, Regions, Fauna, Flora
Rupee, Bombay Stock Exchange, National Stock Exchange, Standard of living, Companies, Reserve Bank of India, Energy policy (Solar, Wind, Nuclear), Tourism, Transport (Expressways, Rail transport, Auto rickshaw),
Languages, Standard of living, Religion
Music (Carnatic, Hindustani, Indi-pop), Dance, Languages, Literature, Architecture, Film & TV, Cuisine, Holidays, Folklore, Education, Media, Indian martial arts
Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), Indian Institute of Astrophysics, National Centre for Software Technology, AIIMS, IISc, IIT, NIT, BITS-Pilani, INRegistry, Indian numbering system, Indian Space Research Organisation, National Internet Exchange of India, ICRISAT, International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad
Indian English, Indian nationality law, Numbering system, Indian Space Research Organisation, Telecommunications, National Highways Development Project, Flag, Vehicle registration plates, Indian nationalism, Metrication in India
Categories
Related portals
Religions in India
Indian Subcontinent
Other countries
Wikipedias in Indian languages
- অসমীয়া (Assamese)
- বাংলা (Bengali)
- भोजपुरी (Bhojpuri)
- বিষ্ণুপ্রিয়া মণিপুরী (Bishnupriya Manipuri)
- गोंयची कोंकणी / Gõychi Konknni (Konkani)
- ગુજરાતી (Gujarati)
- हिन्दी (Hindi)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- कॉशुर/كشميري (Kashmiri)
- मैथिली (Maithili)
- മലയാളം (Malayalam)
- मराठी (Marathi)
- नेपाली (Nepali)
- नेपाल भाषा
- (Newari)
- ଓଡ଼ିଆ (Odiya)
- ਪੰਜਾਬੀ (Punjabi)
- पालि (Pali)
- संस्कृत (Sanskrit)
- ᱥᱟᱱᱛᱟᱲᱤ (Santali)
- سنڌي (Sindhi)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ತುಳು (Tulu)
- اردو (Urdu)
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
- Pages using the Phonos extension
- Pages with Bengali IPA
- Pages including recorded pronunciations
- Pages with Hindustani IPA
- Pages with Hindi IPA
- Pages with Tamil IPA
- Pages with Sanskrit IPA
- Pages with Marathi IPA
- Portals with triaged subpages from June 2018
- All portals with triaged subpages
- Portals with no named maintainer
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 51–100 articles in article list
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 101–200 articles in article list
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 501–1000 articles in article list
- Wikipedia move-protected portals
- Redirect targets of redirected portals with existing subpages